Журнал «Актуальная инфектология» Том 8, №3, 2020
Вернуться к номеру
Інфекція Helicobacter pylori та вітамін D
Авторы: Сорокман Т.В., Попелюк Н.О., Остапчук В.Г.
ВДНЗ України «Буковинський державний медичний університет», м. Чернівці, Україна
Рубрики: Инфекционные заболевания
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
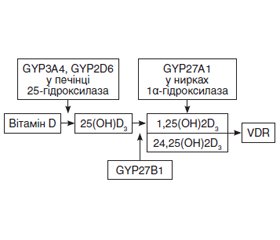
В огляді проаналізовано роль вітаміну D в патогенезі Helicobacter pylori-асоційованих захворювань шлунково-кишкового тракту та його вплив на успіх ерадикаційної терапії. Наведені сучасні дані про механізм взаємодії між вітаміном D, Helicobacter pylori та імунною системою.
В обзоре проанализированы роль витамина D в патогенезе Helicobacter pylori-ассоциированных заболеваний желудочно-кишечного тракта и его влияние на успех эрадикационной терапии. Приведены современные данные о механизме взаимодействия между витамином D, Helicobacter pylori и иммунной системой.
The review examines the role of vitamin D in the pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastrointestinal diseases and its impact on the effectiveness of eradication therapy. Current data on the mechanism of interaction between vitamin D, Helicobacter pylori and the immune system are presented.
Helicobacter pylori; вітамін D; імунна система
Helicobacter pylori; витамин D; иммунная система
Helicobacter pylori; vitamin D; immune system
/8.jpg)
Висновки
- Peng C., Hu Y., Ge Zhong-Ming et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infections in Children and Elderly Populations. Chronic. Dis. Transl. Med. 2020. 5(4). 243-251. doi: 10.1016/j.cdtm.2019.12.003.
- Hooi J.K.Y., Lai W.Y., Ng W.K. et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter Pylori Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology. 2017. 153(2). 420-429. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.04.022.
- Zamani M., Ebrahimtabar F., Zamani V. et al. Systemati Review With Meta-Analysis: The Worldwide Prevalence of Helicobacter Pylori Infection Aliment Pharmaco Ther. 2018. 47(7). 868-876. DOI: 10.1111/apt.14561.
- Malfertheiner P., Megraud F., O’Morain C.A. et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection — the Maastricht V/Florence consensus report. Gut. 2017. 66(1). 6-30. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312288.
- Liu W.Z., Xie Y., Lu H. et al. Fifth Chinese National Consensus Report on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 2018. 23(2). e12475. doi: 10.1111/hel.12475.
- Kalach N., Bontems P., Raymond J. Helicobacter Pylori Infection in Children Helicobacter. 2017. 22(12). 3. doi: 10.1111/hel.12414.
- Melby K.K., Carlsen L.K., Håland G. et al. Helicobacter pylori in early childhood and asthma in adolescence. BMC Research Notes. 2020. 13. 1. Doi: 10.1186/s13104-020-04941-6.
- Cisarò F., Pizzol A., Pinon M., Calvo P.L. Diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori in the pediatric population. Minerva Pediatrica. 2018. 70. 5. Doi: 10.23736/S0026-4946.18.05346-X.
- Sokwala A., Shah M.V., Devani S., Yonga G. Helicobacter pylori eradication: a randomised comparative trial of 7-day versus 14-day triple therapy. S. Afr. Med. J. 2012. 102(6 Pt. 2). 368-371. doi: 10.7196/samj.5302.
- Chen L., Xu W., Lee A. et al. The impact of Helicobacter pylori infection, eradication therapy and probiotic supplementation on gut microenvironment homeostasis: An open-label, randomized clinical trial. BioMedicine. 2018. 3. 5. 87-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.08.028.
- D’Elios M.M., Czinn S.J. Immunity, Inflammation, and Vaccines for Helicobacter Pylori. Helicobacter. 2014. 19(1). 19-26. doi: 10.1111/hel.12156.
- Абатуров О.Є., Герасименко О.М. Модуляція активності TLR4 епітеліоцитів слизової оболонки шлунка при хелікобактерній інфекції (огляд літератури). Современная педиатрия. 2009. 6(28). 141-146.
- Dixon B.R., Hossain R., Patel R.V., Scott H.M. Al good Th17 Cells in Helicobacter Pylori Infection: A Dichotomy of Help and Harm. Infect. Immun. 2019. 87 (11). 122. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00363-19.
- Bagheri N., Salimzadeh L., Shirzad H. The Role of T Helper 1-cell Response in Helicobacter Pylori-Infection. Microb. Pathog. 2018. 123. 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.06.033.
- Dixon B.R., Radin J.N., Piazuelo M.B. et al. IL-17a and IL-22 Induce Expression of Antimicrobials in Gastrointestinal Epithelial Cells and May Contribute to Epithelial Cell Defense Against Helicobacter Pylori. PLoS One. 2016. 11(2). e0148514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148514.
- Sanaii A., Shirzad H., Haghighian M. et al. Role of Th22 Cells in Helicobacter Pylori-Related Gastritis and Peptic Ulcer Diseases. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019. 46(6). 5703-5712. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-05004-1.
- Bagheri N., Shirzad H., Mirzaei Y. et al. T-bet+ Cells Polarization in Patients Infected With Helicobacter Pylori Increase the Risk of Peptic Ulcer Development. Arch. Med. Res. 2019. 50(3). 113-121. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2019.07.005.
- Lu Y.C. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 2008. 42(2). 145-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.01.006.
- Brandt S., Kwok T., Hartig R., König W., Backert S. NF-kappaB activation and potentiation of proinflammatory responses by the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005. 102(26). 9300-5.
- Yang Z.M., Chen W.W., Wang Y.F. Gene expression profiling in gastric mucosa from Helicobacter pylori-infected and uninfected patients undergoing chronic superficial gastritis. PLoS One. 2012. 7(3). e33030. doi: 10.1371/journal. pone.0033030.
- Bagheri N., Salimzadeh L., Shirzad H. The Role of T Helper 1-cell Response in Helicobacter Pylori-Infection. Microb. Pathog. 2018. 123. 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.06.033.
- Kim S.Y., Min C.H., Oh D.J., Choi H.G. Reciprocal association between depression and peptic ulcers: two longitudinal follow-up studies using a national sample cohort. Sci. rep. 2020. 10(1). 1749. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58783-0.
- Hernández C., Serrano C., Einisman H. et al. Peptic Ulcer Disease in Helicobacter Pylori-Infected Children: Clinical Findings and Mucosal Immune Response. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014. 59(6). 773-8. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000500.
- Darma A., Nugroho B.S.T., Yoanna V. et al. Comparison of Helicobacter pylori Stool Antigen, Salivary IgG, Serum IgG, and Serum IgM as Diagnostic Markers of H.pylori Infection in Children. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2019. 11(3). 206-211. Jun 2019.
- Абатуров О.Є., Герасименко О.М. Структурна організація факторів уродженого імунітету в розвитку запалення слизової оболонки шлунка при H.pylori-інфекції у дітей. Здоровье ребенка. 2015. 1(60). 77-80.
- Baeke F., Takiishi T., Korf H., Gysemans C., Mathieu C. Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010 Aug. 10(4). 482-96. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.001.
- Aranow C. Vitamin D and the immune system. J. Investig. Med. 2011. 59(6). 881-886. doi: 10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755.
- Korf H., Decallonne B., Mathieu C. Vitamin D for infections. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2014 Dec. 21(6). 431-6. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000108.
- El Shahawy M.S., Hemida M.H., El Metwaly I., Shady Z.M. The effect of vitamin D deficiency on eradication rates of Helicobacter pylori infection. JGH Open. 2018. 2(6). 270-275.
- Вертегел А.А., Овчаренко Л.С. Вплив недостатності вітаміну D на стан імунної системи: подвійна небезпека розвитку порушень остеогенезу в дітей, хворих на рекурентний бронхіт. Перинатология и педиатрия. 2015. 3(63). 7174. Doi: 10.15574/PP.2015.63.71.
- Zosky G.R., Berry L.J., Elliot J.G. Vitamin D deficiency causes deficits in lung function and alters lung structure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011. 183(10). 1336-1343.
- Magnus M.C., Stene L.C., Haberg S.E. Prospective study of maternal mid-pregnancy 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and early childhood respiratory disorders. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2013. 27(6). 532-541.
- Saraf R., Morton S.M., Camargo C.A.J., Grant CC. Global summary of maternal and newborn vitamin D status — a systematic review. Matern. Child Nutr. 2016. 12(4). 647-68. doi: 10.1111/mcn.12210.
- Рекомендации по поступлению витамина D и лечению его дефицита в Центральной Европе. Журн. Гродненского мед. ун-та. 2014. 2. 109-118.
- Holick M.F. The vitamin D deficiency pandemic: Approaches for diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017. 18. 153-165. doi: 10.1007/s11154-017-9424-1.
- Дефіцит та недостатність вітаміну D: епідеміологія, діагностика, профілактика та лікування. За ред. проф. В.В. Поворознюка, проф. П. Плудовські. Донецьк: Видавець Заславський О.Ю. 2014. 262 с.
- Квашнина Л.В. Иммуномодулирующие эффекты витамина D у детей. Здоровье ребенка. 2013. 7. 134-139.
- Scolletta S., Colletti M., Di Luigi L., Crescioli C. Vitamin D receptor agonists target CXCL10: new therapeutic tools for resolution of inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. 1. 876319.
- Rizzoli R., Boonen S., Brandi M.I. Review vitamin D upplementation in elderly or postmenopausal women: a 2013 update of the 2008 recomendations from the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO). Current. Medical. Research. & Opinion. 2013. 29. 1-9.
- Han C., Ni Z., Yuan T. et al. Influence of serum vitamin D level on Helicobacter pylori eradication: A multi-center, observational, prospective and cohort study. J. Dig. Dis. 2019. 20. 421-426. 10.1111/1751-2980.12793.
- Cantorna T.M., Snyder L., Lin Y.D., Yang L. Vitamin D and 1,25(OH)2D Regulation of T cells Nutrients. 2015. 7(4). 3011-3021. doi: 10.3390/nu7043011.
- Chun R.F., Hernandez I., Pereira R. et al. Differential Responses to Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3 Are Associated With Variations in Free 25-Hydroxyvitamin D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016 Jan. 17(1). 76. Published online 2016 Jan 8. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010076.
- Schwalfenberg G.K. A review of the critical role of vitamin D in the functioning of the immune system and the clinical implications of vitamin D deficiency. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011. 55(1). 96-108.
- Youssef D.A., Miller C.W.T., El-Abbassi A.M. et al. Antimicrobial implications of vitamin D. Dermatoendocrinol. 2011. 3(4). 220-229.
- Wang G., Narayana J., Mishra B. et al. Antimicrobial Peptides: Progress Made With Human Cathelicidin LL-37. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019. 11(17). 215-240. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-3588-4_12.
- Penna G., Adorini L. Alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 Inhibits Differentiation, Maturation, Activation, and Survival of Dendritic Cells Leading to Impaired Alloreactive T Cell Activation. J. Immunol. 2000. 164(5). 2405-11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.5.2405.
- Ginde A.A., Mansbach J.M., Camargo C.A. Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and upper respiratory tract infection in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009. 169(4). 384-390.
- Zosky G.R., Berry L.J., Elliot J.G. Vitamin D deficiency causes deficits in lung function and alters lung structure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011. 183(10). 1336-1343.
- De La Puente-Yagüe M., Cuadrado-Cenzual M.A., Ciudad-Cabañas M.J. et al. Vitamin D: And Its Role in Breast Cancer Kaohsiung. J. Med. Sci. 2018. 34(8). 423-427. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2018.03.004.
- Yin X., Sun Q., Zhang X. et al. Serum 25(OH)D is inversely associated with metabolic syndrome risk profile among urbanmiddle-aged Chinese population. Nutr. J. 2012. 11. 68-75.
- Alberti K.G.M.M., Zimmet P., Shaw J. Metabolic syndrome — a new world-wide definition. A consensus statement from the international diabetes federation. Diabet. Med. 2006. 23. 469-480.
- Yildirim O., Yildirim T., Seckin Y. et al. The influence of vitamin D deficiency on eradication rates of Helicobacter pylori. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017. 26(9). 1377-1381.
- Dankers W., Colin E.M., van Hamburg J.P. et al. Vitamin D in Autoimmunity: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Front. Immunol. 2016. 7. 697. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00697.
- Chen N., Wan Z., Han S.F. et al. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on the Level of Circulating High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Nutrients. 2014 Jun. 6(6). 2206-2216. Published online 2014 Jun 10. doi: 10.3390/nu6062206.
- Kawaura A., Takeda E., Tanida N. et al. Inhibitory effect of long term 1. ALPHA-Hydroxyvitamin D3 administration on Helicobacter pylori infection. J. of Clin. Biochemistry and Nutrition. 2006. 38(2). 73-76. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.38.103.
- Antico A., Tozzoli R., Giavarina D. et al. Hypovitaminosis D as predisposing factor for atrophic type A gastritis: a case-control study and review of the literature on the interaction of Vitamin D: a case-controlstudy and review of the literature on the interaction of Vitamin D with the immune system. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2012. 42. 355-364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s1201 6-011-8255-1.
- Yildirim O., Yildirim T., Seckin Y. et al. The influence of vitamin D deficiency on eradication rates of Helicobacter pylori. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017. 26. 1377-1381. https://doi.org/10.17219 /acem/65430.
- Wang T.T., Nestel F.P., Bourdeau V. et al. Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression. J. Immunol. 2004. 173. 2909-2912.
- Ramanathan B., Davis E.G., Ross C.R. et al. Cathelicidins: microbicidal activity, mechanisms of action, and roles in innateimmunity. Microbes Infect. 2002. 4. 361-372.
- Wehkamp J. et al. Defensins and Cathelicidins in Gastrointestinal Infections. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. Jan 2007. 23(1). 32-8. DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e32801182c2.
- Pero R., Coretti L., Nigro E. et al. 12β-Defensins in the Fight Against Helicobacter Pylori. Molecules. 2017. 22(3). 424. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030424.
- Christakos S., Dhawan P., Verstuyf A. et al. Carmeliet Vitamin D: Metabolism, Molecular Mechanism of Action, and Pleiotropic Effects. Physiol. Rev. 2016. 96(1). 365-408. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00014.2015.
- Wanibuchi K., Hosoda K., Ihara M. et al. Indene compounds synthetically derived from vitamin D have selective antibacterial action on Helicobacter pylori. Lipids. 2018. 53(4). 393-401.
- Inamo Y., Hasegawa M., Saito K. et al. Serum vitamin D concentrations and associated severity of acute lower respiratory tract infections in Japanese hospitalized children. Pediatrics International. 2011. 53(2). 199-201.
- Gois P.H.F., Ferreira D., Olenski S., Seguro A.C. Vitamin D and infectious diseases: Simple bystander or contributing factor? Nutrients. 2017. 9. 651 doi: 10.3390/nu9070651.
- Del Pinto R., Ferri C., Cominelli F. Vitamin D Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Role, Current Uses and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017. 18(11). 12. doi:10.3390/ijms18112360.
- Shimomura H., Hosoda K., Hayashi S. et al. Steroids mediate resistance to the bactericidal effect of phosphatidylcholines against Helicobacter pylori. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009. 301(1). 84-94.
- Shimomura H., Hosoda K., Hayashi S. et al. Phosphatidylethanolamine of Helicobacter pylori: function as a steroid-binding lipid in the assimilation of free-cholesterol and 3β-hydroxl steroids into the bacterial cell membrane. J. Bacteriol. 2012. 194(10). 2658-2667.
- Guo L., Chen W., Zhu H. et al. Helicobacter pylori induces increased expression of the vitamin d receptor in immune responses. Helicobacter. 2014. 19. 37-47. https://doi.org/10.1111/hel.12102.
- Yildirim O., Yildirim T., Seckin Y. et al. The influence of vitamin D deficiency on eradication rates of Helicobacter pylori. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017. 26. 1377-1381. https://doi.org/10.17219/acem/65430.

/7.jpg)