Вступ
Основною метою лікування хворих на генералізований пародонтит є елімінація мікробного біофільму на поверхні коренів зубів. Біофільм являє собою організовану структуру, що складається з колоній мікроорганізмів, вбудованих у матрикс, який з часом мінералізується і перетворюється на зубний камінь [1]. Мікроорганізми біофільму шляхом селективної адгезії прикріплюються до поверхні кореня і продукують ендотоксини, які спричиняють токсичний вплив на цемент кореня зуба та викликають мікроциркуляторні порушення в тканинах пародонта, пошкоджуючи його структурні елементи.
Цемент — мінералізована тканина, яка покриває корінь зуба і забезпечує разом із періодонтальною зв’язкою прикріплення зубів до альвеолярної кістки [2]. Хронічний запальний процес у тканинах пародонта викликає руйнування періодонтальної зв’язки й оголення поверхні кореня зуба. У результаті впливу факторів навколишнього середовища цемент кореня зазнає як структурних змін, так і змін його елементного хімічного складу, які можуть негативно позначитися на регенерації тканин пародонта, в тому числі і цементу. Пошкодження цементу кореня зубів негативно впливають на функціонування комплексу «альвеолярна кістка — періодонтальна зв’язка — цемент кореня».
Відповідно до різниці щільності клітин та органічних волокон у матриксі цемент кореня гістологічно поділяється на п’ять типів [3]. Безклітинний неволокнистий цемент складається з матриксу, але не містить колагенових волокон і клітин, відкладається у вигляді ізольованих плям на незначних ділянках емалі та дентину і не виконує жодної функції в прикріпленні зубів.
Безклітинний зовнішній волокнистий цемент розміщується в ділянці шийки та у верхніх двох третинах кореня зуба, складається з мінералізованого матриксу та великої кількості колагенових волокон, впорядкованих у щільні пучки, одні з яких розміщуються паралельно поверхні цементу, інші мають радіальний напрямок. З одного боку вони переходять у волокна основної речовини дентину, з іншого — у пучки колагенових волокон періодонтальної зв’язки і далі — у шарпеєвські волокна альвеолярної кістки. Велика кількість волокон вказує на значну роль цього різновиду цементу в прикріпленні зубів до кісткової тканини. Товщина безклітинного цементу кореня повільно збільшується з віком [3, 4].
Клітинний внутрішній волокнистий цемент розміщується в ділянці верхівки коренів зубів і ділянці фуркацій та характеризується наявністю цементобластів, цементоцитів і власних колагенових волокон. Цементоцити розміщуються в лакунах і мають відростки, що орієнтовані в бік періодонту, який є джерелом трофіки шляхом дифузії. Цементобласти знаходяться на поверхні цементу та відповідають за відкладання нових шарів цементу. Клітинний внутрішній волокнистий цемент відіграє важливу роль у регенерації цементу, виявляється в дефектах резорбції та місцях переломів коренів [3, 4]. Клітинний змішаний багатошаровий цемент є комбінацією клітинного внутрішнього волокнистого цементу та безклітинного внутрішнього волокнистого цементу, шари яких накладаються один на одний [2].
При генералізованому пародонтиті елімінація мікробного біофільму досягається завдяки згладжуванню та поліруванню твердих поверхонь коренів зубів із застосуванням ручних і механічних інструментів: ультразвукових і звукових скалерів і кюрет. Застосування тих чи інших видів інструментів має значний вплив на поверхню кореня зуба, яка контамінована мікроорганізмами. Під час інструментальної обробки поверхні кореня є низка факторів, що впливають на товщину цементу: тип і потужність скалера, дизайн насадок, гострота робочої частини кюрети, прикладена сила й адаптація інструментів до поверхні кореня (кути нахилу). Органічний матрикс цементу подібний до матриці кісткової тканини: цементобласти експресують білки кісткової матриці — остеокальцин, остеопонтин і сіалопротеїн; крім того, у мінералізованій матриці цементу виділяються фактори росту: тромбоцитарний фактор росту, інсуліноподібний фактор росту, трансформуючий фактор росту бета-1, основний фактор росту фібробластів та інші білки, в результаті чого цемент кореня зуба відіграє важливу роль у регенерації тканин пародонта і створенні нового прикріплення, тому неагресивна робота на поверхні коренів зубів у пародонтологічних пацієнтів є необхідною для забезпечення оптимального пародонтального здоров’я [4, 5].
Одним із ключових елементів досягнення успішної регенерації тканин пародонта є делікатна робота в під’ясенній ділянці та запобігання розвитку пошкоджень цементу кореня при підтримувальному пародонтологічному лікуванні, коли інструментальна робота збільшує ризик руйнування цементу кореня зуба.
Метою даного дослідження було вивчити вплив механічної обробки поверхні коренів зубів на товщину цементу при проведенні пародонтологічного лікування у пацієнтів із генералізованим пародонтитом.
Матеріали та методи
Клінічне дослідження. До дослідження було включено 14 пацієнтів із діагнозом «генералізований пародонтит II та III ступеня тяжкості, хронічний перебіг», на етапі первинного пародонтологічного лікування у яких було видалено 24 однокореневих зуби за пародонтологічними й ортопедичними показаннями (за інформованою згодою). Для встановлення діагнозу генералізованого пародонтиту використовували класифікацію М.Ф. Данилевського (1994). Учасникам було проведено рентгенологічне (ортопантомограма) та пародонтологічне обстеження з використанням клініко-інструментальної програми Florida Probe system (Florida Probe Corp, Gainesville, FL).
Ультраструктурне дослідження проводили на 24 однокореневих зубах верхньої і нижньої щелеп, видалених за пародонтологічними й ортопедичними показаннями. За допомогою скануючого електронного мікроскопа Tescan Mira 3 LMU (TESCAN ORSAY HOLDING, Czech Republic) проводили вимірювання товщини цементу верхньої третини коренів зубів на 48 поздовжніх шліфах, отриманих з 24 однокореневих зубів у хворих на генералізований пародонтит до проведення первинного пародонтологічного лікування та після різних видів інструментальної обробки.
Проведено 4 серії досліджень, по 6 зубів у кожній, залежно від впливу на поверхню кореня зубів. До I серії досліджень включено видалені зуби за пародонтологічними показаннями (ІІІ ступінь рухомості) після проведення пародонтологічного лікування з використанням магнітострикційного ультразвукового скалера Сavitron (Dentsply Sirona, USA). До II серії досліджень було включено зуби, поверхню яких було оброблено магнітострикційним ультразвуковим скалером Cavitron та зоноспецифічними кюретами Грейсі. III серія досліджень включала зуби, поверхня яких була оброблена зоноспецифічними кюретами Грейсі. IV серія досліджень становила контрольну групу, яка включала 6 зубів з генералізованим пародонтитом, поверхня яких не підлягала інструментальному впливу.
Протокол підготовки зразків зубів. Зразки зубів були занурені в 2,5% розчин глутарового альдегіду на 24 години та оброблені гіпохлоритом натрію для видалення органічних відкладень. Проведено зневоднення зразків за стандартним гістологічним протоколом у серіях етанолу зростаючої концентрації (25%, 50%, 70%, 100% по 12 годин), після чого проводилось висушування зразків у критичній точці CO2. Для отримання поздовжніх шліфів зубів зразки були залиті в епоксидну смолу. Поздовжні шліфи зубів в епоксидних блоках одержували на приладі Metcon MicraCut 151 (Metkon, Turkey). Шліфи полірували з використанням абразивної пасти, закріплювали на столики за допомогою провідного адгезивного вуглецевого матеріалу та покривали тонким шаром сплаву Au/Pd товщиною 30 нм в установці Gatan 682 PECS (Gatan, Germany). За допомогою скануючого електронного мікроскопа Tescan Mira 3 LMU, який обладнаний енергодисперсійним спектрометром Oxford X-Max 80 mm2, при прискорюючій напрузі 10 кВ на поздовжніх шліфах зубів проводили морфометричні виміри та вивчали товщину цементу верхньої третини коренів зубів.
Статистичний аналіз був проведений за допомогою мови програмування R (версія 3.6.3). Для представлення показників товщини цементу кореня зубів використовували середнє значення та стандартне відхилення (M ± SD). Статистичне значення між групами визначали за методом Краскела — Волліса. Для множинних порівнянь застосовували метод Холма. Статистично значущою різницю вважали при рівні p < 0,05.
Результати та обговорення
До дослідження було включено 14 хворих на генералізований пародонтит ІІ та ІІІ ступеня тяжкості.
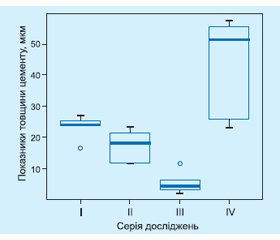
За результатами морфометрії цементу (на поздовжніх шліфах) встановлено, що товщина цементу верхньої третини коренів зубів IV серії становила 44,09 ± 15,32 мкм. У зразків I серії досліджень середня товщина цементу верхньої третини коренів становила 23,56 ± 3,63 мкм, тоді як товщина цементу коренів зубів III серії досліджень була 17,40 ± 4,82 мкм. Товщина цементу коренів зубів IV серії досліджень була найнижчою, її середні показники становили 5,47 ± ± 3,35 мкм (рис. 1).
/18.jpg)
Наявна вірогідна різниця товщини цементу верхньої третини коренів зубів між зразками IV та III серії досліджень (p = 0,013). Вірогідна різниця товщини цементу верхньої третини коренів зубів спостерігалася між зразками IV та II серії досліджень (p = 0,013). Між зразками III та I серії досліджень також була наявна вірогідна різниця товщини цементу кореня (p = 0,020). Вірогідна різниця товщини цементу верхньої третини коренів спостерігалася між зразками III та II серії досліджень (p = 0,020). Між зразками IV та I серії досліджень, а також між зразками I та II серії досліджень вірогідна різниця товщини цементу верхньої третини коренів зубів близька до вірогідної (p = 0,065, p = 0,061 відповідно) (рис. 2).
/19.jpg)
Дослідження проводилось на видалених зубах у пацієнтів із генералізованим пародонтитом на етапі первинного пародонтологічного лікування. За допомогою методу електронної мікроскопії виявлено значний вплив механічного інструментарію на поверхню цементу коренів зубів. Результати дослідження показали, що робота магнітострикційним ультразвуковим скалером усувала менше цементу порівняно з зоно-специфічними кюретами Грейсі. Ці дані узгоджуються з дослідженнями, проведеними Bozbay et al. та Ritz et al. [6, 7]. У пацієнтів із генералізованим пародонтитом цемент кореня зубів тонший, тому під час інструментальної обробки поверхні коренів зубів можна видалити цемент разом із нижчеприлеглим дентином, що призведе до оголення дентинних трубочок. Враховуючи наявність біологічно активних медіаторів, які входять до складу кісткової тканини і цементу кореня, постійний інструментальний вплив на поверхню цементу кореня може призвести до значної втрати його товщини та втрати біомеханічних особливостей, які відіграють значну роль у процесах фіксації та регенерації пародонтального комплексу.
Висновки
1. Товщина цементу коренів зубів (на поздовжніх шліфах), які оброблялися зоноспецифічними кюретами Грейсі, була найнижчою, її середні показники становили 5,47 ± 3,35 мкм, тоді як товщина цементу верхньої третини коренів зубів, які не підлягали інструментальному впливу, була 44,09 ± 15,32 мкм.
2. Під час проведення первинного пародонтологічного лікування робота магнітострикційного ультра-звукового скалера показала менший вплив на товщину цементу коренів зубів порівняно із застосуванням зоноспецифічних кюрет Грейсі (p = 0,020).
3. Пошкодження цементу кореня зубів у хворих на генералізований пародонтит є структурною основою низького регенераторного потенціалу цементу, що пояснюється особливостями безклітинного цементу у пришийковій ділянці, втратою клінічного прикріплення ясен і впливом мікроорганізмів. Вірогідне зменшення товщини цементу коренів зубів у поєднанні з підвищеним жувальним навантаженням внаслідок травматичної оклюзії та низькими регенеративними властивостями цементу пришийкової частини кореня зуба є чинником розвитку гіперестезії та цервікальних уражень.
Конфлікт інтересів. Автор заявляє про відсутність конфлікту інтересів та власної фінансової зацікавленості при підготовці даної статті.
Отримано/Received 16.11.2021
Рецензовано/Revised 26.11.2021
Прийнято до друку/Accepted 02.12.2021
/19.jpg)

/18.jpg)