Журнал «Почки» Том 14, №1, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Нирки: уромодулін і гіперурикемія
Авторы: Денова Л.Д. (1), Джаббарлі І.(2)
(1) - Національний університет охорони здоров’я України ім. П.Л. Шупика, м. Київ, Україна
(2) - Національний медичний університет імені О.О. Богомольця, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Нефрология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
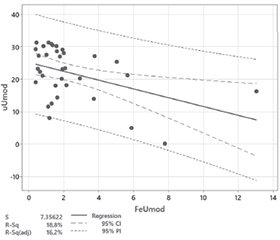
Актуальність. Уромодулін (Umod) має значний вплив на розвиток і перебіг хронічної хвороби нирок (ХХН). Наприклад, вищий рівень Umod асоціюється з більшими розмірами нирки та розрахунковою швидкістю клубочкової фільтрації (рШКФ). Відомо, що екскреція Umod пов’язана з фракційною екскрецією сечової кислоти (UrAc), хлориду та натрію (маркерами об’ємного перевантаження), але ще не до кінця з’ясований зв’язок між Umod і гіперурикемією. Мета: дослідити зв’язок між рівнями UrAc крові та Umod у пацієнтів з ХХН І–ІІІ стадії. Матеріали та методи. Було проведене проспективне рандомізоване когортне дослідження ROLUNT (uROmoduLin, UbiquinoNe, glutaThione), у якому взяли участь 34 пацієнти з рівнем sUrAc більше за 360 мкмоль/л, у 2021–2023 рр. Дослідження ROLUNT проводилося у ТОВ «ВЕТА-ПЛЮС» та КДЦ Броварської багатопрофільної клінічної лікарні, що є клінічними базами кафедри нефрології та НЗТ Національного університету охорони здоров’я України імені П.Л. Шупика. Результати. Результати кореляції Спірмена показали, що в групі (n = 34) існує значний великий позитивний зв’язок: між фракційною екскрецією Umod (FeUmod) та індексом ризику розвитку термінальної стадії ХХН через 2 роки (QxMD2) і через 5 років (QxMD5); між індексом Чарлсона (ІЧ), креатиніном крові (sCrea), азотом сечовини (BUN), сечовиною крові (sUrea), ліпопротеїдами низької щільності (LDL), загальним холестерином (sChol), Umod сечі (uUmod)/рШКФ за формулою CKD-EPI (рШКФCKD), uUmod/креатиніном сечі (uCrea), альбуміном сечі (uAlb)/uCrea; між uAlb/uUmod та uAlb, uAlb/uCrea; між добовим uUmod (uUmod24) та uUmod, uUmod/Umod крові (sUmod), індексом маси тіла (ІМТ); між uUmod/sUmod та uUmod, uUmod24; між uUmod/uCrea та uAlb/uCrea, uUmod/рШКФCKD, FeUmod, sChol, LDL, ліпопротеїдами дуже низької щільності (VLDL), відсотком жирової тканини (ЖТ), sUrea, BUN, BUN/sCrea, sUrea/sCrea, QxMD2, QxMD5; між uUmod/рШКФCKD та uUmod/uCrea, FeUmod, sUrea, BUN, sCrea, QxMD2, QxMD5. Висновки. Широке коло впливу uUmod не тільки на сечовидільну систему робить його важливим біомаркером в клінічній практиці нефрологів, а також лікарів інших спеціальностей.
Background. Uromodulin (Umod) has a significant impact on the development and course of chronic kidney disease (CKD). For example, a higher Umod level is associated with larger kidney size and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Umod excretion is known to be associated with fractional excretions of uric acid, chloride, and sodium (markers of volume overload), but the relationship between Umod and hyperuricemia is not yet fully understood. The purpose of the study: to investigate the relationship between blood uric acid levels and Umod in patients with CKD stage I–III. Materials and methods. A prospective randomized cohort ROLUNT (uROmoduLin, UbiquinoNe, glutaThione) study in which 34 patients with blood uric acid levels greater than 360 μmol/L participated was conducted in 2021–2023. The ROLUNT study was carried out at VETA-PLUS LLC and the Brovary Multidisciplinary Clinical Hospital, which are the clinical bases of the Department of Nephrology and Renal Replacement Therapy of the Shupyk National Healthcare University of Ukraine. Results. The results of Spearman’s correlation showed that there is a significant large positive relationship: between the fractional excretion of Umod (FeUmod) and the risk index for the development of the terminal stage of CKD after 2 (QxMD2) and 5 years (QxMD5); the Charlson Comorbidity Index, blood creatinine (sCrea), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), blood urea (sUrea), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), total cholesterol (sChol), urine Umod (uUmod)/eGFR according to the CKD-EPI formula (eGFRCKD), uUmod/urine creatinine (uCrea), urinary albumin (uAlb)/uCrea; between uAlb/uUmod and uAlb, uAlb/uCrea; between daily uUmod (uUmod24) and uUmod, uUmod/Umod of blood (sUmod), body mass index; between uUmod/sUmod and uUmod, uUmod24; between uUmod/uCrea and uAlb/uCrea, uUmod/eGFRCKD, FeUmod, sChol, LDL, very low density lipoprotein, percentage of adipose tissue, sUrea, BUN, BUN/sCrea, sUrea/sCrea, QxMD2, QxMD5; between uUmod/eGFRCKD and uUmod/uCrea, FeUmod, sUrea, BUN, sCrea, QxMD2, QxMD5. Conclusions. The wide range of effects of uUmod not only on the urinary system makes it an important biomarker in the clinical practice of nephrologists and doctors of other specialties.
хронічна хвороба нирок; ультразвукове дослідження нирок; сечова кислота; уромодулін
chronic kidney disease; kidney ultrasound; uric acid; uromodulin
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Denova LD, Ivanov DD. Assessment of the risk of rapid progression of chronic kidney disease. Kidneys. 2024;13(4):250-256. doi: 10.22141/2307-1257.13.4.2024.480.
- Liu Y, Goldfarb DS, El-Achkar TM, Lieske JC, Wu XR. Tamm-Horsfall protein/uromodulin deficiency elicits tubular compensatory responses leading to hypertension and hyperuricemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Jun 1;314(6):F1062-F1076. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00233.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 10. PMID: 29357410; PMCID: PMC6032075.
- Barr SI, Abd El-Azeem EM, Bessa SS, Mohamed TM. Association of serum uromodulin with diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2024 Nov 24;25(1):421. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03854-x. PMID: 39581971; PMCID: PMC11587581.
- Takata T, Isomoto H. The Versatile Role of Uromodulin in Renal Homeostasis and Its Relevance in Chronic Kidney Disease. Intern Med. 2024 Jan 1;63(1):17-23. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1342-22. Epub 2023 Jan 15. PMID: 36642527; PMCID: PMC10824655.
- Micanovic R, LaFavers K, Garimella PS, Wu XR, El-Achkar TM. Uromodulin (Tamm-Horsfall protein): guardian of urinary and systemic homeostasis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2020 Jan 1;35(1):33-43. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy394. PMID: 30649494; PMCID: PMC8205501.
- Liyanarachi KV, Flatby H, Hallan S, Еsvold BO, Damеs JK, Rogne T. Uromodulin and Risk of Upper Urinary Tract Infections: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2025 Jan 11:S0272-6386(25)00009-5. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2024.11.007. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39805364.
- Chen TK, Estrella MM, Appel LJ, Surapaneni AL, Kцttgen A, Obeid W, Parikh CR, Grams ME. Associations of Baseline and Longitudinal Serum Uromodulin with Kidney Failure and Morta–lity: Results from the African American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension (AASK) Trial. Am J Kidney Dis. 2024 Jan;83(1):71-78. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2023.05.017. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690632.
- Ikeme JC, Scherzer R, Garimella PS, Hallan SI, Katz R, Estrella MM, Ix JH, Shlipak MG. The Association of Plasma and Urine Uromodulin With Cardiovascular Disease in Persons With Hypertension and CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 2024 Dec;84(6):799-802. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2024.05.012. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 39033957.
- Xiong L, Wu C, Chen S, Zhang Y, Wang L, Li Y, Li G. Proteomics analysis reveals age-related proteins in the urine of chronic kidney disease patients. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 6;11:1506134. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1506134. PMID: 39835101; PMCID: PMC11743183.
- Денова Л.Д. Значення протеомних досліджень новітніх маркерів ураження нирок у сечі для оцінки перебігу, прогресування й ускладнень у пацієнтів із ХХН. Нирки. 2022;2(11):7-20. doi: https://doi.org/10.22141/2307-1257.11.2.2022.363. URL: http://www.mif-ua.com/archive/article/51908.
- Denova LD. Development of renal fibrosis in patients with chronic kidney disease: Mechanisms, biomarkers, and clinical implications. Ukr. J. of Nephrology and Dialysis. 2023;3(79):54-67. doi: https://doi.org/10.31450/ukrjnd.3(79).2023.08 [In Ukrainian]. URL: https://ukrjnd.com.ua/index.php/journal/article/view/771/436.
- Karagiannidis AG, Theodorakopoulou MP, Pella E, Sarafidis PA, Ortiz A. Uromodulin biology. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024 Jun 28;39(7):1073-1087. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfae008. PMID: 38211973; PMCID: PMC11210992.
- Bullen AL, Vaingankar S, Madero M, Lopez Gil S, Macedo E, Ix JH, Rifkin DE, Garimella PS. Urine Uromodulin, Kidney Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis, and Furosemide Response. Nephron. 2024;148(7):443-447. doi: 10.1159/000534578. Epub 2023 Dec 1. PMID: 38043509; PMCID: PMC11216347.
- Wu CH, Yang CC, Chang HW, Huang B, Chen CJ, Lin EI, Wu CY, Chung YH, Hsu YH, Lee CT, Chuang FR. Urinary Uromo–dulin/Creatinine Ratio as a Potential Clinical Biomarker for Chronic Kidney Disease Patients with Gout: A Pilot Study. Med Princ Pract. 2019;28(3):273-279. doi: 10.1159/000496844. Epub 2019 Jan 13. PMID: 30636243; PMCID: PMC6597938.
- Gou R, Dou D, Tian M, Chang X, Zhao Y, Meng X, Li G. Association between triglyceride glucose index and hyperuricemia: a new evidence from China and the United States. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 1;15:1403858. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1403858. PMID: 39010899; PMCID: PMC11246899.
- Du L, Zong Y, Li H, Wang Q, Xie L, Yang B, Pang Y, Zhang C, Zhong Z, Gao J. Hyperuricemia and its related diseases: mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Aug 28;9(1):212. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01916-y. PMID: 39191722; PMCID: PMC11350024.
- Kim GH, Jun JB. Altered Serum Uric Acid Levels in Kidney Disorders. Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;12(11):1891. doi: 10.3390/life12111891. PMID: 36431026; PMCID: PMC9692609.
- George C, Leslie SW, Minter DA. Hyperuricemia. 2023 Oct 14. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2024 Jan. PMID: 29083565.
- Ahn EY, So MW. The pathogenesis of gout. J Rheum Dis. 2025 Jan 1;32(1):8-16. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2024.0054. Epub 2024 Nov 6. PMID: 39712248; PMCID: PMC11659655.
- Ivanov D, Ivanova M, Bevzenko T. Febuxostat Improves GFR and BP in Non-Diabetic Adults With CKD 2–3: 6 Years Treatment and Follow-up. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 2018;33(5):i626. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy104.SuO025.
- Li Y, Zeng L. Comparison of seven anthropometric indexes to predict hypertension plus hyperuricemia among U.S. adults. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Mar 8;15:1301543. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1301543. PMID: 38524637; PMCID: PMC10958198.
- Li C, Li J, Diao Z, Chen L, Yu S, Yu L, Zhu Q, Dong X, Liu Y, Liu T, Liu D. Associations of dietary choline intake and kidney function with hyperuricemia in Chinese children and adolescents: a cross-sectional study. EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Dec 17;79:103012. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103012. PMID: 39802309; PMCID: PMC11720878.
- Zhang Y, Liu X, Luo D, Chen B, Lai C, He C, Yan L, Ding H, Li S. Association of LDL-C/HDL-C Ratio With Hyperuricemia: A National Cohort Study. Clin Transl Sci. 2025 Jan;18(1):e70122. doi: 10.1111/cts.70122. PMID: 39780404; PMCID: PMC11711105.
- Liang Y, Qiao T, Ni X, Yang L, Yao T, Liu Y. Association between hyperuricemia and dietary retinol intake in Southwest China: a cross-sectional study based on CHNS database. Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 22;12:1508774. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1508774. PMID: 39911811; PMCID: PMC11794100.
- Yang H, Ying J, Zu T, Meng XM, Jin J. Insights into renal damage in hyperuricemia: Focus on renal protection (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2025 Mar;31(3):59. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13424. Epub 2024 Dec 24. PMID: 39717954; PMCID: PMC11711934.
- Zhang WZ, Peng Q, Cai XS, Jiang GL, Huang JJ, Lu LL, Feng WZ, Yan PY, Gu JR. A study on the correlation between hyperuricemia and lifestyle and dietary habits. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jan 31;104(5):e41399. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041399. PMID: 39889152; PMCID: PMC11789900.
- Peng H, Han Y, Huang J, Qiu W, Chang H, Fang J, Peng XE. Inverse relationship of oxidative balance score with hyperuricemia among Chinese adults: a population-based cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 20;25(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21419-x. PMID: 39833759; PMCID: PMC11744993.
- Barnini C, Russo E, Leoncini G, Ghinatti MC, Macciт L, Piaggio M, Viazzi F, Pontremoli R. Asymptomatic Hyperuricemia and the Kidney: Lessons from the URRAH Study. Metabolites. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):11. doi: 10.3390/metabo15010011. PMID: 39852354; –PMCID: PMC11767115.
- Melchinger H, Calderon-Gutierrez F, Obeid W, Xu L, Shaw MM, Luciano RL, Kuperman M, Moeckel GW, Kashgarian M, Wilson FP, Parikh CR, Moledina DG. Urine Uromodulin as a Biomarker of Kidney Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 Sep;17(9):1284-1292. doi: 10.2215/CJN.04360422. Epub 2022 Aug 10. PMID: 35948365; PMCID: PMC9625093.
- Kong L, Li Y, Zhu R, Guo M, Wu Y, Zhong Y, Li Z, Xiong Z. Association between serum uric acid, hyperuricemia and low muscle mass in middle-aged and elderly adults: A national health and nutrition examination study. PLoS One. 2025 Jan 7;20(1):e0312235. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312235. PMID: 39775063; PMCID: PMC11706472.