Журнал «Боль. Суставы. Позвоночник» Том 15, №2, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Вплив дистального блокування на рівень напружень металофіксатора при остеосинтезі черезвертлюгових переломів (експериментальне моделювання)
Авторы: Калашніков А.В., Сабарна Ю.Х.М.
ДУ «Інститут травматології та ортопедії НАМН України», м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Ревматология, Травматология и ортопедия
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
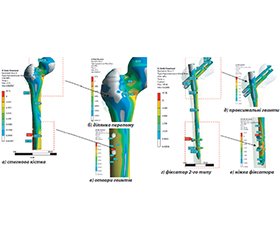
Актуальність. У розвинутих країнах світу в лікуванні переломів проксимального відділу стегнової кістки широко впроваджують малоінвазивні технології застосування проксимального стегнового стрижня. Проте ми не знайшли літературних даних щодо напружень на блокований інтрамедулярний (ІМ) стрижень залежно від типу перелому за класифікацією Асоціації остеосинтезу та варіантів його дистального блокування. Мета дослідження: провести аналіз напружень на різні металеві фіксатори при виконанні остеосинтезу з приводу черезвертлюгових переломів типу А2. Матеріали та методи. Використовували макет стегнової кістки, у який імплантовано фіксуючі елементи. Для фіксації відламків застосовували інтрамедулярні блокуючі стрижні у 3 варіантах фіксації: за допомогою одного, двох гвинтів або за відсутності блокуючих гвинтів у дистальній частині стрижня. Розрахунки напружено-деформованого стану методом кінцевих елементів проводили для інтактної моделі з обома варіантами фіксаторів, а потім з фіксаторами при черезвертлюгових переломах типу А2 та варіантами дистального блокування (без блокування, 1 гвинтом, 2 гвинтами). Результати. Мінімальне напруження на металеві фіксатори в їх проксимальних відділах визначали при застосуванні PFN (проксимальний феморальний стрижень) у варіанті з застосуванням 2 гвинтів для дистального блокування. Ці дані статистично вірогідно відрізнялися від даних при застосуванні PFN-стрижня без дистального блокування. На дистальний відділ металевих фіксаторів напруження було мінімальне при застосуванні PFN-стрижня з використанням 2 гвинтів для дистального блокування (195,27 МPа). Визначено, що мінімальна, але адекватна для цього типу вертикально та ротаційно нестабільного перелому мікрорухливість (2,17 мм) спостерігалася при використанні моделі PFN-стрижня із застосуванням 2 гвинтів для дистального блокування. Ці мікрорухи сприятимуть поліпшенню репаративного остеогенезу черезвертлюгових переломів типу А2. Занадто велика мікрорухливість при застосуванні моделей без та із використанням 1 блокуючого гвинта для дистального блокування PFN-стрижня (2,27 та 2,23 мм) може призвести до порушення репаративного остеогенезу при застосуванні цього методу металофіксації. Висновки. Проведене дослідження визначає диференційований підхід до лікування хворих із черезвертлюговими переломами стегнової кістки, що поліпшить ефективність надання медичної допомоги такій тяжкій категорії хворих.
Background. In developed countries, minimally invasive technologies for using the proximal femoral rod are widely implemented in treating fractures of the proximal femur. However, we did not find literature data on the stresses on the blocked intramedullary rod depending on the type of fracture due to the Association of Osteosynthesis and variants of its distal blocking. The study aimed to carry out biomechanical modelling of stresses on various metal fixators during osteosynthesis for transtrochanteric fractures of type A2. Materials and methods. A femoral model with implanted fixation elements was used. Intramedullary locking rods were used to fix the fragments in 3 fixation options: with one, two screws, or without locking screws in the distal part of the rod. Calculations of the stress-strain state using the finite element method were performed for the intact model with both types of fixators, and then for fixators used in transtrochanteric fractures of type A2, with options for distal locking (without locking, one screw, two screws). Results. The minimum tension on the metal retainers in their proximal parts was determined when using the PFN (proximal femoral nail) in the variant with two screws for distal locking. These data were statistically significantly different from the data when the PFN-rod was used without distal locking. On the distal part of the metal retainers, the stress was minimal when applying the PFN-rod with the use of 2 screws for distal locking (195.27 MPa). It was determined that minimal but adequate micromobility for this vertically and rotationally unstable fracture was observed when using the PFN model of the rod, with the use of 2 screws for distal locking (2.17 mm). These micromovements will contribute to the improvement of reparative osteogenesis in patients with transtrochanteric type A2 fractures. Excessive micromobility may occur when using the model without and with one locking screw for distal locking of the PFN rod (2.27 and 2.23 mm), potentially leading to impaired reparative osteogenesis with this method of metal fixation. Conclusion. Our research suggested a differentiated approach to treating patients with transcavitary fractures of the femur, which is expected to enhance the effectiveness of medical care for this severe patient category.
моделювання; переломи; напруження; остеосинтез, лікування
modelling; fracture; tension; osteosynthesis; treatment
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Поворознюк В.В., Григор’єва Н.В., Корж М.О., Страфун С.С., Каніс Д.A., Макклоскі Є.В., Форосенко В.С. Епідеміологія переломів проксимального відділу стегнової кістки в Україні: результати двох ретроспективних досліджень. Ортопедия, травматология и протезирование. 2016;4:68-74. doi: 10.15674/0030-59872016468-74.
- Saltvedt I, Prestmo A, Einarsen E, Johnsen LG, Helbostad JL, Sletvold O. Development and delivery of patient treatment in the Trondheim Hip Fracture Trial. A new geriatric in-hospital pathway for elderly patients with hip fracture. BMC Res. Notes. 2012;5:355. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-355.
- Kanis JA, Odén A, McCloskey EV, Johansson H, Wahl DA, Cooper C. IOF Working Group on Epidemiology and Quality of Life. A systematic review of hip fracture incidence and probability of fracture worldwide. Osteoporosis international. 2012;23(9):2239-2256. doi: 10.1007/s00198-012-1964-3.
- Choy WS, Kim KJ, Lee SK, Yang DS, Jeung SW, Choi HG, Park HJ. Surgical treatment of pathological fractures occurring at the proximal femur. Yonsei medical journal. 2015;56(2):460-465. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.2.460.
- Walter N, Szymski D, Kurtz S, Alt V, Lowenberg DW, Lau E, Rupp M. Factors associated with mortality after proximal femoral fracture. Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology. 2023;24:31. doi: 10.1186/s10195-023-00715-5.
- Піонтковський В.К., Денисюк Б.С., Малевич Ю.М., Каштан Ю.М., Циплінський Ю.І., Златів В.П., Столярський Н.І. Наш досвід малоінвазивного остеосинтезу при черезвертлюжних переломах стегнової кістки. Травма. 2012;13(4):140-142.
- Smektala R, Endres HG, Dasch B, Maier C, Trampisch HJ, Bonnaire F, Pientka L The effect of time-to-surgery on outcome in elderly patients with proximal femoral fractures. BMC musculoskeletal disorders. 2008;9:171. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-9-171.
- Kijima H, Yamada S, Konishi N, Kubota H, Tazawa H, Tani T, Suzuki N, Kamo K, Okudera Y, Sasaki K, Kawano T, Shimada Y. The Reliability of Classifications of Proximal Femoral Fractures with 3-Dimensional Compu–ted Tomography: The New Concept of Comprehensive Classification. Advances in Orthopedics. 2014;2014:359689. doi: 10.1155/2014/359689.
- Fischer H, Maleitzke T, Eder C, Ahmad S, Stockle U, Braun KF. Management of proximal femur fractures in the elderly: current concepts and treatment options. Eur J. Med Res. 2021;26:86. doi: 10.1186/s40001-021-00556-0.
- Ding K, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Wang H, Li J, Chen W, Zhang Q. Proximal femoral bionic nail — a no–vel internal fixation system for the treatment of femoral neck fractures: a finite element analysis Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023;11:1297507. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1297507.
- Sadic S, Custovic S, Jasarevic M, Fazlic M, Smajic N, Hrustic A, Vujadinovic A, Krupic F. Proximal femoral nail antirotation in treatment of fractures of proximal femur. Medicinski arhiv. 2014;68(3):173-177. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2014.68.173-177.
- Liu H, Yuan B, Yu T, Ren G, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Liu Y, Peng C, Wu D. Accurate fixation of complicated comminuted femur fracture with customized LCP referencing a life-size 3D-printed model. Annals of Translational Medicine. 2020;8(7):505. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.03.115.
- Калашніков А.В., Сабарна Ю.Х.М. Результати експериментального моделювання напружень на фіксатори при металоостеосинтезі черезвертлюгових переломів. Біль. Суглоби. Хребет. 2024;14(4):33-41. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.22141/pjs.14.4.2024.442.
- Маланчук В.О., Крищук М.Г., Копчак-Маланчук А.В. Імітаційне комп’ютерне моделювання в щелепно-лицевій хірургії. 2013. К.: Асканія: 45-49.
- Никифоров Р.Р., Куценко С.Н., Костандов Ю.А. Механико-математическая модель системы металлоостеосинтеза и расчет ее напряженно-деформированного состояния. Травма. 2013;14(3):43-51.
- Mostafa IA, El-Sayed Abdel-Aal SA, Yassin MO. Proximal Femoral Plate Versus Proximal Femoral Nailing Fixation for Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fe–moral Fractures. Al-Azhar International Medical Journal. 2024;5(193):206. doi: 10.58675/2682-339X.2282.
- Rosa N, Moura MFSF, Olhero S, Simoes R, Magalhaes FD, Marques AT. Bone: an outstanding composite material. Appl Sci. 2022;12:3381. doi: 10.3390/app12073381.
- Cisneros T, Sevostianov I, Drach B. Elasticity and material anisotropy of lamellar cortical bone in adult bovine tibia characterized via AFM nanoindentation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023;144:105992. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2023.105992.
- Bittner-Frank M, Reisinger AG, Andriotis OG, Pahr DH, Thurner PJ. Cortical and trabecular mechanical properties in the femoral neck vary differently with changes in bone mineral density. JBMR Plus. 2024;8(6):ziae049. doi: 10.1093/jbmrpl/ziae049.
- Katnic I, Orlandic MI. Fundamentals of Biomedical Statistics. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2020;274:111-121. doi: 10.3233/SHTI200671.
- Molinari G, Emiliani N, Cercenelli L, Bortolani B, Gironi C, Javier I, Presutti FL, Marcelli E. Assessment of a novel patient-specific 3D printed multi-material simulator for endoscopic sinus surgery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022;17(10):974021. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.974021.
- Zaczyk M, Jasińska-Choromańska D. Contact phenomena modeling in biological structures on the example of the implant-bone. Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures. 2019:16(1 Thematic Section):e172. doi: 10.1590/1679-78254955.
- Tretiakow D, Tesch K, Markiet K. Numerical ana–lysis of the ostiomeatal complex aeration using the CFD method. Scientific Reports. 2023;13:1-11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31166-x.
- Galbusera F, Cina A, Panico M, Albano D, Messina C. Image-based biomechanical models of the musculoskeletal system. European Radiology Experimental. 2020;4:49. doi: 10.1186/s41747-020-00172-3.