Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» 1 (64) 2015
Вернуться к номеру
Ultrasound regional block anesthesia for carotid endarterectomy
Авторы: Strokan A.M. - P. L. Shupyk National Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education, Kyiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
The article represents the method of ultrasound regional block anesthesia for carotid endarterectomy.
carotid endarterectomy, cervical plexus block.
Ischemic stroke, as a result of atherosclerotic carotid arterial involvement, is one of the main causes of incapacitation and mortality under elderly people. Surgical treatment of patients suffering from constrictive and deformans lesions of extracranial internal carotid artery parts is the most effective method of ischemic stroke prevention at present (International Randomized Studies NASCET, ECST, ACAS) [4].
Whereas according to the data of world literature, regional anesthesia by carotid endarterectomy allows to evaluate neurological functions (level of consciousness, language functions, range of movements in the extremities in real time) in the process of carotid artery clamping and throughout the surgery, and other evaluation methods of cerebral blood supply (transcranialdopplerography, cerebral oxygenation, electro-encephalography) are an additional way to assess the functional status of the brain. We had been implemented regional anesthesia in this type of surgery. [2,5].
In November, 2014 the regional anesthesia technique during surgery carotid endarterectomywas initiated and performedby 3 patientsin the FeofaniyaClinical Hospital.The techniqueconsisted in a deep and ultrasound-guided superficial cervical plexus blocks.
Most researchers recommend for this surgery to perform both deep and superficial cervical plexus blocks. Furthermore, the surgical team should perform during surgery thelocal anesthesia for carotid body [1,2].
Cervical plexus innervates the anterior lateral surface of theneck, superficial branches innervate the skin, deep branches – the muscles (Figure 1.)
Figure 1.Image of cervical plexus.
- lesser occipital nerve;
- great auricular nerve;
- transverse cervical nerve;
- supraclavicular nerves;
The superficial cervical plexus block was performed by solution injection of the local anesthetic Ropivacaine 0.5% - 10ml subcutaneously on the posterior edge of sternocleidomastoid muscle at the level C4-C5 [1].
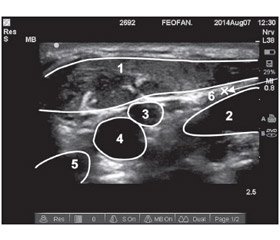
The deep cervical plexus block is performed on the posterior edge of the middle of sternocleidomastoid muscle at the level C4. Linear array transducer with high frequency (12-18 mHz) is set perpendicular to sternocleidomastoid muscle at the level C7 and glides to the level C4. There is a division of the common carotid artery at this level in most patients. The solution of Ropivacaine 0.5% - 20 ml is injected by sternocleidomastoid muscle in the space between it, the muscle that lifting the scapula, and the middle scalene muscle. That is the space between the deep and superficial cervical fascia, where the nerve trunks permeate (Figure 2). There is used the needle Stimuplex A 50mm for block[1].
Figure 2.Ultrasound anatomy of deep cervical plexus block.
- sternocleidomastoid muscle;
- middle scalene muscle:
- internal jugular vein;
- internal carotid artery;
- external carotid artery;
- injection point for local anesthetic.
Conclusion.Operative intervention of carotid endarterectomy can be performed under regional anesthesia of superficial and deep cervical plexus with the possibility to assess neurological functions of the patient during surgery. The use of ultrasound imaging makes the procedure safe and effective.

/163/163.jpg)