Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» 4 (64) 2015
Вернуться к номеру
Optimization of physical activity of children in the context of prevention of cardiovascular risk
Авторы: Chaychenko T. - Kharkiv National Medical University, Kharkiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
physical activity, children, prevention, cardiovascular health
The paper provides a review of current regulatory documents of international organizations in terms of optimizing of physical activity of children.
It is shown that the main causes of mortality in the World are cardiovascular problems and its’ complications (by WHO, 2015), which strongly associated with obesity with an onset in childhood. Almost all of such death should be considered as premature. Over 90% of these premature deaths occur in low- and low middle-income countries. Ukraine is in the last group by The World Bank rate. Probability to die prematurely for Ukrainians between 30 and 70 y.o. is 28%.
There is a tendency to obesity epidemic as number of overweight adults has increased by 27,5 % and children by 47,1 % from 1980 to 2013. It is proved that a cardiovascular risk reduction happens successfully when use non-medicament inter v entions such as lifestyles and diet correction. The same time sedentary lifestyle is the main cause of low energy expenditures in paediatric and adolescent population. Physical inactivity leads to the weight gain even in those who keep diet strictly.
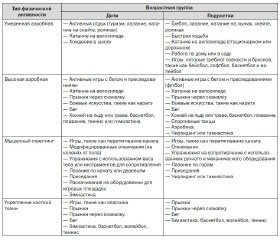
It’s recommended to engage kids to exercising since infancy. All toddlers should not be sedentary for more than 60 minutes except when sleeping. There is necessary to combine planned activity (with an instructor) and not-planned activity, which helps with development of competence in fundamental motor skills that will serve as building blocks for future motor skillfulness and physical activity.
By The WHOUNICEF (2008) recommendation the individual protection such as helmets, knee pads, etc. should be mentioned when engaging to high intensity activity to reduce the risk of traumatic injuries among children.
Analysis the results of The Commission on Ending Childhood Obesity (WHO, 2015) with a focus at the necessity of multi sectoral governmental, educational and social activities is presented. Family should be involved to exercising as there is not possible to reach adequate activity level for child just at school time (by the American Heart Association, 2014).