Резюме
Об’єкт дослідження: хворі з бактеріальними менінгоенцефалітами. Методи: клінічне спостереження, обернено-фазова високоефективна рідинна хроматографія з ультрафіолетовим детектуванням; методи статистичного аналізу й логіки.
Публікація присвячена дослідженню концентрації меропенему в лікворі хворих при різних способах введення: внутрішньовенному та комбінованому (внутрішньовенне + інтратекальне). Підтверджена безпека інтратекального застосування дози 100–200 мг меропенему + 8 мг дексаметазону. При інтратекальному введенні 100–200 мг меропенему встановлено статистично значиме підвищення концентрації меропенему в лікворі на період не менше доби.
Объект исследования: больные с бактериальными менингоэнцефалитами. Методы: клиническое наблюдение, обратно-фазовая высокоэффективная жидкостная хроматография с ультрафиолетовым детектированием; методы статистического анализа и логики.
Публикация посвящена исследованию концентрации меропенема в ликворе больных при различных способах введения: внутривенном и комбинированном (внутривенное + интратекальное). Подтверждена безопасность интратекального применения дозы 100–200 мг меропенема + 8 мг дексаметазона. При интратекальном введении 100–200 мг меропенема установлено статистически значимое повышение концентрации меропенема в ликворе на период не менее суток.
The object of the study: patients with bacterial meningoencephalitis. Methods: clinical observation, reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection; methods of statistical analysis and logic.
The publication is devoted to the study of meropenem concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients in different ways of administration: intravenous and combined (intravenous + intrathecal). The safety of intrathecal use of a dose of 100–200 mg of meropenem + 8 mg of dexamethasone was confirmed. In intrathecal administration of 100–200 mg meropenem, we have found a statistically significant increase in the concentration of meropenem in the cerebrospinal fluid for a period of not less than one day.
Introduction.
The protective properties of the blood–brain barrier lead to a significant decrease in the concentration of antibacterial drugs in the central nervous system, and blood–brain barrier is completely impermeable for some of them. Modification of dose and dose regime of drugs is proposed for optimization of neuroinfection treatment. In our opinion, a possible way for increasing the effectiveness of treatment is intrathecal administration of antibacterial drugs.
Only single reports of successful intrathecal use of meropenem in the treatment of meningoencephalitis were found by us in the available scientific literature that is indicative of insufficient attention to this problem.
The safety of intrathecal meropenem administration that permitted to pass to the clinical stage was established by our previous studies on animals.
Object.
To study the difference of meropenem concentration in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) after intravenous and combined (intravenous + intrathecal) ways of drug administrations.
Materials and Methods
The study was conducted in 10 treated HIV–negative patients aged 18 to 68 years (7 men and the 3 women) with bacterial meningoencephalitis, including four patients with tuberculous meningoencephalitis.
Selection of the CSF samples for the first (before intrathecal therapy) measurement of the meropenem concentration was performed at least in 48 hours after intravenous meropenem administration at a dose of 1–2 g, 4 times per day. Selection of the CSF samples for the second concentration measurement were made in the same patient in twenty-four hours after intrathecal meropenem administration in a dose 100–200 mg with 8 mg dexamethasone.
The study to determine the meropenem concentration in cerebrospinal fluid were performed by the method of feed-back phase high–performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with ultraviolet detection.
Results.
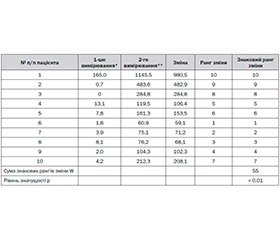
Meropenem concentration in cerebrospinal fluid after intrathecal administration exceeded the previous level of the drug (before intrathecal administration) in all cases.
|
Patients |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
The first measurement mcg / cm3 |
165,0 |
0,7 |
0 |
13,1 |
7,8 |
1,8 |
3,9 |
8,1 |
2,0 |
4,2 |
|
The second measurement mcg / cm3 |
1145,5 |
483,6 |
284,8 |
119,5 |
161,3 |
60,9 |
75,1 |
76,2 |
104,3 |
212,3 |
W = 55, for n = 10. The level of significance p <0.01 using Wilcoxon test.
The obtained results are indicative of the statistically significant increase of meropenem concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients even in twenty-four hours after intrathecal administration of drug in a dose of 100–200 mg. It is logical to assume that meropenem concentration in cerebrospinal fluid was even greater immediately after administration.
It is important to note, that irritating effect of drug as a moderate increase in heart rate (20% of the initial one) and involuntary movements of the lower extremities were occurred after the intrathecal administration of meropenem solution in two cases. The reaction was not prolonged (up to 2 minutes), and additional treatment was not required. In both cases, the side effect was appeared in a case when the concentration of administered solution exceeded 10 mg / mL, and was not dependent on the total dose of the drug. Any adverse events were registered at the next survey during twenty-four hours that once again demonstrates the safety of proposed way for drug administration.
CONCLUSIONS
1. Intrathecal administration of 100–200 mg meropenem with 8 mg dexamethasone is safe.
2. Concentration of meropenem solution for intrathecal administration should not exceed 10 mg / ml to avoid the irritating action.
3. Intrathecal administration of 100–200 mg meropenem with 8 mg dexamethasone in combination with intravenous drug administration leads to the statistically significant increase of meropenem concentration in cerebrospinal fluid at least during twenty-four hours after the injection.
4. Intrathecal administration of meropenem with dexamethasone in the proposed doses can be recommended for the treatment of bacterial meningoencephalitis caused by organisms susceptible to meropenem.
5. In the case of initial empirical therapy of bacterial meningoencephalitis with intravenous meropenem, an additional treatment with intrathecal meropenem administration and dexamethasone is recommended in the proposed doses for increasing the efficiency and preventing the development of antibiotic-resistance.
6. Intrathecal therapies should be only used by specialists of relevant qualifications.
Список литературы
1. Андреева И.В. Место меропенема в терапии тяжелых инфекций / И.В. Андреева, О.У. Стецюк // Клиническая фармакология и терапия. — 2008. — Т. 17, № 2. — С. 19-27.
2. Борщов С.П. Експериментальне дослідження безпечності інтратекального застосування меропенему з дексаметазоном / С.П. Борщов, І.В. Фільчаков, П.В. Сініцин, Н.М. Серединська // Фармакологія та лікарська токсикологія. — 2013. — № 3 (34). — С. 35-40.
3. Внелегочный туберкулез / Под ред. А.В. Васильева. — СПб., 2000. — 499 с.
4. Гебеш В.В. Гнійний менінгоенцефаліт — прогноз перебігу та особливості етіотропної терапії / В.В. Гебеш, О.Л. Коляда, П.В. Чегусов // Український медичний часопис. — 2009. — № 6. — С. 73-76.
5. Кононенко В.В. Нові можливості етіотропного лікування гнійних менінгоенцефалітів меропенемом / В.В. Кононенко // Сучасні інфекції. — 1999. — № 2. — С. 117-121.
6. Нейрореаниматология. Интенсивная терапия черепно-мозговой травмы / Под ред. С.В. Царенко. — М.: Медицина, 2006. — 352 с.
7. Antimicrobial activity of meropenem against main bacterial species isolated from patient blood in 2010 / Y. Kobayashi, Y. Sumitani, R. Inose, Y. Katohno // Jpn. J. Antibiot. — 2011. — Vol. 64, № 6. — P. 355-365.
8. A liquid chromatography assay for a quantification of doripenem, ertapenem, imipenem, meropenem concentrations in human plasma: application to a clinical pharmacokinetic study / E. Dailly, R. Bouquie, G. Deslandes [et al.] // J. Chromatogr. B-аnalyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. — 2011. — Vol. 879, № 15–16. — P. 1137-1142.
9. Baldwin C.M. Meropenem: a review of its use in the treatment of serious bacterial infections / C.M. Baldwin, K.A. Lyseng-Williamson, S.J. Keam // Drugs. — 2008. — Vol. 68, № 6. — P. 803-838.
10. Hawkey P.M. Carbapenem antibiotics for serious infections / P.M. Hawkey, D.M. Liverore // BMJ. — 2012. — Vol. 344. — P. 32-36.
11. HPLC method for measuring meropenem and biapenem concentrations in human peritoneal fluid and bile: application to comparative pharmacokinetic investigations / K. Kameda, I. Kazuro, I. Kayo [et al.] // J. Chromatogr. Sci. — 2010. — Vol. 48. — P. 406-411.
12. LC Method for the determination of meropenem in cerebrospinal fluid: application to therapeutic drug monitoring / Tomoko Matsuda, Kazuro Ikawa, Kayo Ikeda [et al.] // Chromatographia. — 2009. — Vol. 69, № 9–10. — P. 1031-1034.
13. Meropenem prevents levofloxacin-induced resistance in penicillin-resistant pneumococci and acts synergistically with levofloxacin in experimental meningitis / P. Cottagnoud, F. Acosta, L. Flatz [et al.] // Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. — 2003. — Vol. 22, № 11. — P. 656-662.
14. Nicolau D.P. Carbapenems: a potent class of antibiotics / D.P. Nicolau // Expert Opin. Pharmacother. — 2008. — Vol. 9, № 1. — P. 23-37.
15. Obtain best usage of meropenem dose in severe infections. Results of an observational multicenter study / B. Alvarez-Sánchez, F. Alvarez-Lerma, J. Romero [et al.] // Rev. Esp. Quimioter. — 2008. — Vol. 21, № 3. — P. 143-148.
16. Perrott J. Comparing outcomes of meropenem administration strategies based on pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic principles: A qualitative systematic review / J. Perrott, V.H. Mabasa, M.H. Ensom // The Ann. Harmacotherapy. — 2010. — Vol. 44. — P. 557-564.