Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 17, №2, 2022
Вернуться к номеру
Механізми дії цитоплазматичних мікроРНК. Частина 1. Механізми взаємодії молекул мікроРНК і мРНК. Вплив мікроРНК на трансляцію
Авторы: Абатуров О.Є., Бабич В.Л.
Дніпровський державний медичний університет, м. Дніпро, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
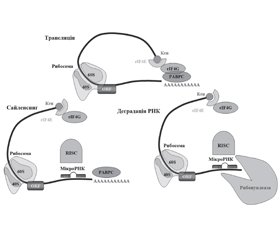
В науковому огляді наведені механізми дії цитоплазматичних мікроРНК, а саме взаємодії молекул мікроРНК і мРНК, і вплив мікроРНК на трансляцію. Для написання статті здійснювався пошук інформації з використанням баз даних Scopus, Web of Science, MedLine, PubMed, Google Scholar, EMBASE, Global Health, The Cochrane Library, CyberLeninka. Авторами показано, що для взаємодії мікроРНК і мРНК потрібна наявність у регіоні 3’-кінця молекули мРНК невеликих нуклеотидних послідовностей — регуляторних елементів мікроРНК (miRNA regulatory element, MRE), які комплементарні послідовностям seed-ділянки (seed — англ. «насіння, зерно») мікроРНК. Відомо, що для ініціації взаємодії мікроРНК з мРНК-мішенню необхідно лише шість нуклеотидних збігів у seed-ділянці (положення 2–8). Підкреслено, що взаємодія мікроРНК з мРНК залежить від доступності сайту зв’язування мРНК. Автори зазначають, що у процесі взаємодії мікроРНК і мРНК беруть участь аксесуарні протеїни. Відомо, що процес гібридизації мРНК і мікроРНК залежить від наявності SNP. Науковці вважають, що основною функцією цитоплазматичних мікроРНК є регуляція активності синтезу білків. Зазначено, що мікроРНК можуть репресувати й активувати процес трансляції мРНК. Крім того, деякі мікроРНК здатні як пригнічувати, так і посилювати трансляцію мРНК залежно від конкретних локальних умов і спектра факторів мікрооточення. Таким чином, механізм дії цитоплазматичних мікроРНК реалізується завдяки взаємодії мікроРНК і мРНК, яка обумовлена наявністю комплементарних одна одній нуклеотидних послідовностей особливих регіонів. Взаємодія мікроРНК з мРНК залежить від доступності сайту зв’язування мРНК, участі аксесуарних протеїнів і наявності SNP. Порушення взаємодій мікроРНК і мРНК призводять до розвитку патологічних процесів. Цитоплазматичні мікроРНК виконують свою основну функцію, а саме регуляцію активності синтезу білків, за рахунок мікроРНК-опосередкованої репресії та активації трансляції мРНК.
The scientific review presents the mechanisms of action of cytoplasmic miRNAs, namely the relationship between miRNA and mRNA molecules and the influence of miRNAs on translation. To write the article, information was searched using Scopus, Web of Science, MEDLINE, PubMed, Google Scholar, Embase, Global Health, The Cochrane Library, CyberLeninka databases. The authors state that the interaction of microRNA and mRNA requires the presence in the region of the 3'-end of the mRNA molecule of small nucleotide sequences — miRNA regulatory elements, which are complementary to the sequences of the “seed” region of microRNA. It is known that only six nucleotide matches in the “seed” region (position 2–8) are required to initiate the interaction of microRNA with the mRNA target. It is emphasized that the interaction of miRNA with mRNA depends on the availability of the mRNA binding site. The authors suggest that accessory proteins are involved in the interaction of microRNA and mRNA. It is known that the process of mRNA and miRNA hybridization depends on the presence of SNP. Scientists believe that the main function of cytoplasmic miRNAs is to regulate the activity of protein synthesis. It is presented that microRNAs can repress and activate the mRNA translation process. In addition, some miRNAs are able to both inhibit and enhance the translation of mRNA depending on specific local conditions and the spectrum of microenvironmental factors. Thus, the mechanism of action of cytoplasmic miRNAs is realized due to the interaction of miRNAs and mRNAs, which is due to the presence of complementary nucleotide sequences of special regions. The interaction of miRNAs with mRNAs depends on the availability of the mRNA binding site, the involvement of accessory proteins, and the presence of SNP. Violations of microRNA-mRNA interactions lead to the development of pathological processes. Cytoplasmic miRNAs perform their main function, namely the regulation of protein synthesis activity, due to miRNA-mediated repression and activation of mRNA translation.
мікроРНК; трансляція мРНК; протеїни Argonaute; огляд
microRNA; miRNA; miR; mRNA translation; Argonaute proteins; review
Вступ
Механізми взаємодії молекул мікроРНК і мРНК
Вплив мікроРНК на трансляцію
Висновки
- Auton A., Brooks L.D., Durbin R.M. et al A global reference for human genetic variation. 1000 Genomes Project Consortium. Nature. 2015 Oct 1. 526(7571). 68-74. doi: 10.1038/nature15393.
- Azlan A., Dzaki N., Azzam G. Argonaute: The executor of small RNA function. J. Genet. Genomics. 2016 Aug 20. 43(8). 481-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2016.06.002.
- Béthune J., Artus-Revel C.G., Filipowicz W. Kinetic analysis reveals successive steps leading to miRNA-mediated silencing in mammalian cells. EMBO Rep. 2012 Aug. 13(8). 716-23. doi: 10.1038/embor.2012.82.
- Catalanotto C., Cogoni C., Zardo G. MicroRNA in Control of Gene Expression: An Overview of Nuclear Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016 Oct 13. 17(10). pii: E1712.
- Detassis S., Grasso M., Del Vescovo V., Denti M.A. MicroRNAs Make the Call in Cancer Personalized Medicine. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2017 Sep 22. 5. 86. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00086.
- Djuranovic S., Nahvi A., Green R. MiRNA-mediated gene silencing by translational repression followed by mRNA deadenylation and decay. Science. 2012 Apr 13. 336(6078). 237-40. doi: 10.1126/science.1215691.
- Fabian M.R., Sonenberg N., Filipowicz W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010. 79. 351-79. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060308-103103.
- Gebremedhn S., Ali A., Hossain M., Hoelker M., Salilew-Wondim D., Anthony R.V., Tesfaye D. MicroRNA-Mediated Gene Regulatory Mechanisms in Mammalian Female Reproductive Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021 Jan 19. 22(2). 938. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020938.
- Iwakawa H.O., Tomari Y. The Functions of MicroRNAs: mRNA Decay and Translational Repression. Trends Cell. Biol. 2015 Nov. 25(11). 651-65. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.07.011.
- Kang H. MicroRNA-Mediated Health-Promoting Effects of Phytochemicals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019 May 23. 20(10). 2535. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102535.
- Karlsen T.H., Lammert F., Thompson R.J. Genetics of liver disease: From pathophysiology to clinical practice. J. Hepatol. 2015 Apr. 62(suppl. 1). S6-S14. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.02.025.
- King V.M., Borchert G.M. MicroRNA Expression: Protein Participants in MicroRNA Regulation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017. 1617. 27-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7046-9_2.
- Li L.J., Leng R.X., Fan Y.G. et al Translation of noncoding RNAs: Focus on lncRNAs, pri-miRNAs, and circRNAs. Exp. Cell. Res. 2017 Dec 1. 361(1). 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.10.010.
- Ma X., Tao R., Li L., Chen H., Liu Z., Bai J., Shuai X., Wu C., Tao K. Identification of a 5-microRNA signature and hub miRNA-mRNA interactions associated with pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2019 Jan. 41(1). 292-300. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6820.
- Manivannan A., Kim J.H., Yang E.Y. et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Approaches in Genome-Wide Discovery of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Markers Associated with Pungency and Disease Resistance in Pepper. BioMed Res. Int. 2018 Jan 9. 2018. 5646213. doi: 10.1155/2018/5646213.
- Meijer H.A., Kong Y.W., Lu W.T. et al. Translational repression and eIF4A2 activity are critical for microRNA-mediated gene regulation. Science. 2013 Apr 5. 340(6128). 82-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1231197.
- Morozova N., Zinovyev A., Nonne N. et al. Kinetic signatures of microRNA modes of action. RNA. 2012 Sep. 18(9). 1635-55. doi: 10.1261/rna.032284.112.
- Nakano M., Nakajima M. Current knowledge of microRNA-mediated regulation of drug metabolism in humans. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018 May. 14(5). 493-504. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2018.1472237.
- Oliveto S., Mancino M., Manfrini N., Biffo S. Role of –microRNAs in translation regulation and cancer. World J. Biol. Chem. 2017 Feb 26. 8(1). 45-56. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v8.i1.45.
- Oulas A., Karathanasis N., Louloupi A. et al. Prediction of –miRNA targets. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015. 1269. 207-29. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2291-8_13.
- Peterson S.M., Thompson J.A., Ufkin M.L. et al. Common features of microRNA target prediction tools. Front. Genet. 2014 Feb 18. 5. 23. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00023.
- Salomon W.E., Jolly S.M., Moore M.J. et al Single-Molecule Imaging Reveals that Argonaute Reshapes the Binding Properties of Its Nucleic Acid Guides. Cell. 2016 Jul 14. 166(2). 517-520. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.048.
- Seok H., Ham J., Jang E.S., Chi S.W. MicroRNA Target Recognition: Insights from Transcriptome-Wide Non-Canonical Interactions. Mol. Cells. 2016 May 31. 39(5). 375-81. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2016.0013.
- Shyu A.B., Wilkinson M.F., van Hoof A. Messenger RNA regulation: to translate or to degrade. EMBO J. 2008 Feb 6. 27(3). 471-81. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601977.
- Thomson D.W., Bracken C.P., Goodall G.J. Experimental strategies for microRNA target identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Sep 1. 39(16). 6845-53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr330.
- Valinezhad Orang A., Safaralizadeh R., Kazemzadeh-Bavili M. Mechanisms of miRNA-Mediated Gene Regulation from Common Downregulation to mRNA-Specific Upregulation. Int. J. Genomics. 2014. 2014. 970607. doi: 10.1155/2014/970607.
- Yu D., Chen S., Li D., Knox B., Guo L., Ning B. FREMSA: A Method That Provides Direct Evidence of the Interaction between –microRNA and mRNA. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020. 2102. 557-566. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0223-2_30.
- Zhang T., Wu Y.C., Mullane P., Ji Y.J., Liu H., He L., Arora A. еt al. FUS Regulates Activity of MicroRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing. Mol. Cell. 2018 Mar 1. 69(5). 787-801.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.02.001.
- Zhao S., Liu M.F. Mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regu–lation. Sci. China C-Life Sci. 2009 Dec. 52(12). 1111-6. doi: 10.1007/s11427-009-0152-y.

/62.jpg)
/63.jpg)
/64.jpg)