Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» Том 19, №4, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Прогностична роль ММП-9 та МПО в пацієнтів зі зниженою швидкістю клубочкової фільтрації після гострого коронарного синдрому
Авторы: A.O. Bilchenko, M.P. Kopytsya, O.V. Petyunina, I.R. Vishnevskaya, Iu.V. Rodionova
SI “L.T. Malaya National Therapy Institute of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine”,
Kharkiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
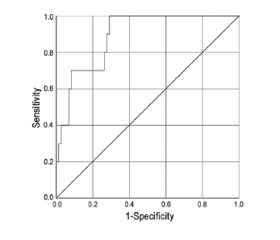
Актуальність. Ішемічна хвороба серця (ІХС) залишається основною причиною смертності в усьому світі. Враховуючи тяжкість та вплив цього захворювання, дослідники ретельно вивчають патогенез атеросклерозу, що є основною причиною ІХС. Етапи патогенезу є складними й багатогранними і включають такі фактори, як акумуляція ліпідів, розвиток запалення і формування бляшок. Особлива сфера активних досліджень стосується впливу на ці процеси й ролі в них різних біомаркерів, включаючи матриксну металопротеїназу-9 (ММП-9) та мієлопероксидазу (МПО). Ці біомаркери пов’язані з прогресуванням і дестабілізацією атеросклеротичних бляшок, що є центральним елементом ІХС. Однак використання цих біомаркерів у контексті супутніх захворювань, таких як хронічна хвороба нирок, залишається відкритою галуззю досліджень, особливо в пацієнтів після інфаркту міокарда. Матеріали та методи. У наше дослідження було включено 96 пацієнтів із гострим коронарним синдромом, які в подальшому перенесли черезшкірне коронарне втручання. Вони були розподілені на групи (А та Б) залежно від показників швидкості клубочкової фільтрації. Первинною кінцевою точкою дослідження була смертність від усіх причин та серйозні небажані серцеві та цереброваскулярні події. Результати. Наш аналіз показав, що сироваткові рівні МПО в групі Б були незначно вищими, ніж у групі А. І навпаки, продемонстровано значну різницю в площі під кривою операційних характеристик приймача (ROC) для ММП-9 в групі А, що становила 0,8 (95% довірчий інтервал 0,609–0,991; p = 0,039). Однак ROC-крива для МПО не дала значущого результату в жодній групі. Також була побудована комбінована ROC-крива, площа під якою показала вірогідно більше значення — 0,890 (95% довірчий інтервал 0,805–0,975; p < 0,001). Висновки. Ми виявили, що рівні вищезгаданих біомаркерів у плазмі крові не впливають на зниження швидкості клубочкової фільтрації. Тим не менш рівень ММП-9 надає значну прогностичну інформацію щодо прогнозованого результату.
Background. Coronary artery disease (CAD) persistently remains the leading cause of mortality globally. Given the severity and impact of this condition, researchers have been meticulously studying the pathogenesis of athe-rosclerosis, a principal cause behind CAD. The pathogenesis stages are complex and multifaceted, including factors such as lipid accumulation, inflammation, and plaque formation. A particular area of active exploration pertains to the influence and role of different biomarkers, including matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) and myeloperoxidase (MPO), on these processes. These biomarkers have been associated with the progression and destabilization of athe-rosclerotic plaques, which are central to CAD. However, the use of these biomarkers in the context of comorbidities, such as chronic kidney disease, remains an open area of research, especially in patients after myocardial infarction. Materials and methods. In our study, 96 patients who had acute coronary syndrome and subsequently undergone percutaneous coronary intervention were enrolled. They were stratified into groups (A and B) based on respective glomerular filtration rates. The primary endpoint of the study was all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. Results. Our analysis revealed that serum levels of MPO in group B were insignificantly higher than those in group A. Conversely, the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for MMP-9 in group A exhibited a significant difference, standing at 0.8 (95% confidence interval 0.609–0.991; p = 0.039). However, the ROC curve for MPO did not yield a significant result in any group. A combined ROC curve was also generated, with the area under this curve showing a significantly higher value of 0.890 (95% confidence interval 0.805–0.975; p < 0.001). Conclusions. We found that plasma levels of the above-mentioned biomarkers do not seem to influence a decrease in glomerular filtration rate. Nonetheless, MMP-9 levels offered significant prognostic information regarding predicted outcomes.
матрикснa металопротеїназa-9; мієло-пероксидазa; гострий коронарний синдром; швидкість клубочкової фільтрації; результат
matrix metalloproteinase 9; myeloperoxidase; acute coronary syndrome; glomerular filtration rate; outcome
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Timmis A., Kazakiewicz D., Townsend N. et al. Global epidemiology of acute coronary syndromes. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023 May 25. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00884-0.
- Fan J., Watanabe T. Atherosclerosis: Known and unknown. Pathol. Int. 2022. 72. 151-160.
- Del Monte-Nieto G., Fischer J.W., Gorski D.J. et al. Basic Bio-
- logy of Extracellular Matrix in the Cardiovascular System, Part 1/4: JACC Focus Seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020. 75. 2169-2188.
- Chen C.Y., Chang F.C., Lee I.H. et al. Involvement of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in vertebral arterial dissection with posterior circulation ischemic stroke. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020 Oct 20. 9(19). e016743. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016743.
- Lahdentausta L., Leskelä J., Winkelmann A. et al. Serum MMP-9 Diagnostics, Prognostics, and Activation in Acute Coronary Syndrome and Its Recurrence. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2018. 11. 210-220.
- Chen X., Meng Y., Shao M. et al. Prognostic value of pre-infarction angina combined with mean platelet volume to lymphocyte count ratio for no-reflow and short-term mortality in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Medical Science Monitor. 2020 Jan 7. 26. e919300. doi: 10.12659/MSM.919300.
- Chen Z., Yan Y., Wu J. et al. Expression level and diagnostic value of exosomal NEAT1/miR-204/MMP-9 in acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. IUBMB Life. 2020. 72. 2499-2507.
- Owolabi U.S., Amraotkar A.R., Coulter A.R. et al. Change in matrix metalloproteinase 2, 3, and 9 levels at the time of and after acute atherothrombotic myocardial infarction. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis. 2020. 49. 235-244.
- Somuncu M.U., Pusuroglu H., Karakurt H. et al. The prognostic value of elevated matrix metalloproteinase-9 in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a two-year prospective study. Revista Portuguesa de Cardiologia. 2020. 39. 267-276.
- Jordakieva G., Budge-Wolfram R.M., Budinsky A.C. et al. Plasma MMP-9 and TIMP-1 levels on ICU admission are associated with 30-day survival. Wien Klin. Wochenschr. 2021. 133. 86-95.
- Phatharajaree W., Phrommintikul A., Chattipakorn N. Matrix metalloproteinases and myocardial infarction. Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 2007. 23. 727-733.
- Zhao H. Matrix metalloproteinases contribute to kidney fibrosis in chronic kidney diseases. World J. Nephrol. 2013. 2. 84.
- Cheng Z., Limbu M.H., Wang Z. et al. MMP-2 and 9 in chronic kidney disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017 Apr 8. 18(4). 776. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040776.
- Rudolph T.K., Wipper S., Reiter B. et al. Myeloperoxidase deficiency preserves vasomotor function in humans. Eur. Heart J. 2012. 33. 1625-1634.
- Devereux R.B., Reichek N. Echocardiographic determination of left ventricular mass in man. Anatomic validation of the method. Circulation. 1977. 55. 613-618.
- Krebber M.M., van Dijk C.G.M., Vernooij R.W.M. et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in extracellular matrix remodeling during left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020. 21. 1-22.
- Valente F.M., De Andrade D.O., Cosenso-Martin L.N. et al. Plasma levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 are elevated in individuals with hypertensive crisis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020. 20(1). 132. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01412-5.
- Xu T.Y., Zhang Y., Li Y. et al. The association of serum inflammatory biomarkers with chronic kidney disease in hypertensive patients. Ren. Failure. 2014. 36. 666-672.
- Odobasic D., Kitching A.R., Holdsworth S.R. Neutrophil-mediated regulation of innate and adaptive immunity: the role of myeloperoxidase. J. Immunol. Res. 2016. 2016. 2349817. doi: 10.1155/2016/2349817.
- Li T., Li X., Feng Y. et al. The Role of Matrix Metalloprotei-nase-9 in Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability. Mediators of Inflammation. 2020. 2020. 3872367. doi: 10.1155/2020/3872367.
- Delporte C., Van Antwerpen P., Vanhamme L. et al. Low-density lipoprotein modified by myeloperoxidase in inflammatory pathways and clinical studies. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. 2013. 971579. doi: 10.1155/2013/971579.