Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 58, №1, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Зміна рівня зонуліну та можливості його корекції у хворих на цироз печінки та печінкову енцефалопатію після СОVID-19
Авторы: Сірчак Є.С., Марошан М.Т., Поляк М.А.
ДВНЗ «Ужгородський національний університет», м. Ужгород, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
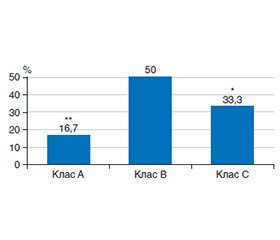
Актуальність. Печінка часто уражається при COVID-19, що може проявлятись від простого підвищення рівня трансаміназ до розвитку гострої печінкової недостатності. Дослідження особливостей перебігу цирозу печінки (ЦП) і його ускладнень, особливо печінкової енцефалопатії (ПЕ), при COVID-19 та дослідження можливих маркерів, що вказують на прогресування захворювання, і розробка ефективних методів їх корекції є актуальним завданням сьогодення. Мета. Вивчити особливості зміни рівня зонуліну в сироватці крові і в калі та його динаміку у хворих на ЦП та ПЕ після СОVID-19 на фоні комплексної терапії з використанням препарату масляної кислоти. Матеріали та методи. Наукове дослідження виконано у два етапи. На І етапі досліджено 126 хворих на ЦП, у яких вивчались особливості перебігу ПЕ, дисбіозу товстої кишки (ДТК) та рівень зонуліну в сироватці крові й калі при виписці хворих зі стаціонару після СОVID-19, а також через 1 місяць амбулаторного спостереження за ними. На ІІ етапі дослідження хворих на ЦП та ПЕ після COVID-19 розподілено на дві групи залежно від проведеного лікування: хворі І групи (n = 56) отримували лише базисну терапію (БТ) ЦП, що включала постійний прийом β-блокатора бісопрололу, лактулози, а також комплексний гепатопротектор та препарат мелатоніну і рифаксимін; пацієнтам ІІ групи (n = 70) додатково до БТ призначено комплексний пробіотичний препарат, що містить масляну кислоту. Результати. Протягом першого місяця після перенесеного COVID-19 у хворих на ЦП діагностовано прогресування вираженості ознак ПЕ. Серед хворих на ЦП класів В і С через місяць після COVID-19 встановлено збільшення кількості пацієнтів із ПЕ ІІ ст. (до 57,2 та 72,2 % відповідно); у 16,7 % хворих з декомпенсованою стадією ЦП діагностовано ПЕ ІІІ ст. Встановлено прогресування вираженості ДТК у хворих з ЦП та ПЕ після COVID-19. Через 1 місяць спостереження при повторному мікробіологічному дослідженні фекалій встановлено вірогідне збільшення кількості пацієнтів з ЦП та ПЕ після COVID-19 незалежно від стадії захворювання з ДТК ІІІ ст., що, відповідно, виникало на фоні зменшення кількості осіб із ДТК І та ІІ ст. У хворих на ЦП та ПЕ після COVID-19 встановлено вірогідне збільшення рівня зонуліну в сироватці крові та в калі з максимальними значеннями у хворих класу С за Child-Pugh, що також мав тенденцію до збільшення протягом першого місяця спостереження (до (171,4 ± 2,2) нг/мл у сироватці крові та до (198,2 ± 3,4) нг/мл у калі). Призначення пробіотичного комплексу, до складу якого входить масляна кислота, сприяло зменшенню рівня зонуліну як у крові, так і в калі у хворих на ЦП та ПЕ після COVID-19 на фоні місячного курсу лікування. Висновки. У хворих на ЦП після COVID-19 діагностовано прогресування вираженості ПЕ, а також ДТК протягом першого місяця амбулаторного спостереження. У хворих на ЦП та ПЕ після COVID-19 встановлено збільшення рівня зонуліну в сироватці крові та калі (до (102,7 ± 1,4) нг/мл (р < 0,01) та (131,4 ± 2,6) (р < 0,001) відповідно), що має тенденцію до збільшення залежно від прогресування тяжкості захворювання. Комплексна терапія з використанням препарату, до складу якого входить масляна кислота, у хворих на ЦП та ПЕ після COVID-19 є ефективним методом для зменшення рівня зонуліну в сироватці крові та калі.
Background. The liver is frequently affected in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which can range from a simple increase in transaminase levels to the development of acute liver failure. The study of the peculiarities of the course of liver cirrhosis (LC) and its complications, especially hepatic encephalopathy (HE), in COVID-19 and the study of possible markers indicating the progression of the disease and the development of effective methods for their correction is an urgent task today. Aim of the research: to study the features of changes in serum and faecal zonulin levels and its dynamics in patients with LC and HE after COVID-19 on the background of a comprehensive therapy with a butyric acid preparation. Materials and methods. The study was conducted in two stages. At the first stage, 126 patients with LC were examined to determine the features of HE course, colonic dysbiosis, and zonulin levels in blood serum and faeces at discharge from the hospital after COVID-19, as well as after 1 month of outpatient follow-up. At the second stage of the study, patients with LC and HE after COVID-19 were divided into two groups depending on the treatment: group I (n = 56) received only basic therapy for LC, which included constant use of the β-blocker bisoprolol, lactulose, as well as a combined hepatoprotective agent, melatonin and rifaximin; group II (n = 70) in addition to basic therapy took a combined probiotic preparation containing butyric acid. Results. During the first month after COVID-19, progression of the HE severity was diagnosed in patients with LC. Among participants with LC classes B and C, an increase in the number of patients with grade II HE (up to 57.2 and 72.2 %, respectively) was found a month after COVID-19, and in 16.7 % of patients with decompensated LC, grade III HE was diagnosed. Colonic dysbiosis progression was detected in patients with LC and HE after COVID-19. In one month of the follow-up, a repeated microbiological examination of faeces revealed a significant increase in the number of patients with LC and HE after COVID-19 with grade III colonic dysbiosis, regardless of the stage of the disease, which, accordingly, occurred against the background of a decrease in patients with grade I and II colonic dysbiosis. Among patients with LC and HE after COVID-19, a significant increase in serum and faecal zonulin was found with maximum values in patients with class C according to the Child-Pugh score, which also tended to increase during the first month of observation (up to (171.4 ± 2.2) ng/ml in serum and up to (198.2 ± 3.4 ng/ml) in faeces). The administration of a probiotic complex containing butyric acid contributed to a decrease in both blood and faecal zonulin levels in patients with LC and HE after COVID-19 during a one-month course of treatment. Conclusions. In patients with LC after COVID-19, a progression of HE and colonic dysbiosis severity was diagnosed during the first month of outpatient follow-up. Participants with LC and HE after COVID-19 reported an increase in the level of zonulin in the blood serum and faeces (up to (102.7 ± 1.4) ng/ml, p < 0.01, and up to (131.4 ± 2.6), p < 0.001, respectively), which tends to increase depending on the progression of the disease severity. Comprehensive therapy with the use of a drug containing butyric acid is an effective method to reduce the level of blood and faecal zonulin in patients with LC and HE after COVID-19.
цироз печінки; печінкова енцефалопатія; СOVID-19; зонулін; дисбіоз товстої кишки; лікування
liver cirrhosis; hepatic encephalopathy; COVID-19; zonulin; colonic dysbiosis; treatment
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- The impact of COVID-19 disease on the natural course of cirrhosis: Before and after starting vaccination / [O. Keskin, H. Oral, T. Sahin, T. Kav, E. Parlak]. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 2. Vol. 9. Р. 1039202.
- COVID-19 and the liver / [D. Jothimani, R. Venugopal, M.F. Abedin, I. Kaliamoorthy, M. Rela]. J Hepatol. 2020 Nov. Vol. 73 (5). Р. 1231-1240.
- Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the care and outcomes of people with NAFLD-related cirrhosis / [J. Rivera-Estban, R. Manzano-Nunez, T. Braquetas et al.]. JHEP. Reports. 2022. Vol. 4. Р. 100574.
- Independent predictors of mortality among patients with NAFLD hospitalized with COVID-19 infection / [Z.M. Younossi, M. Stepanova, B. Lam et al.]. Hepatol Commun. 2022. Vol. 6. Р. 3062-3072.
- Singh A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis / A. Singh, S. Hussain, B. Antony. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021. Vol. 15. Р. 813-822.
- SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with a normal or abnormal liver / [G. Cabibbo, G.E.M. Rizzo, C. Stornello, A. Craxì]. J Viral Hepat. 2021 Jan. Vol. 28 (1). Р. 4-11.
- Vujčić I. Outcomes of COVID-19 among patients with liver disease / I. Vujčić. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. Vol. 29. Р. 815-824.
- Pathophysiological mechanisms of liver injury in COVID-19 / [A.D. Nardo, M. Schneeweiss-Gleixner, M. Bakail, E.D. Dixon, S.F. Lax, M. Trauner]. Liver Int. 2021 Jan. Vol. 41 (1). Р. 20-32.
- Liver, NAFLD and COVID-19 / [C. Hoffmann, P.A. Gerber, C. Cavelti-Weder et al.]. Horm Metab Res. 2022 Aug. Vol. 54 (8). Р. 522-531.
- Ekpanyapong S. COVID-19 and the Liver: Lessons Learnt from the EAST and the WEST, A Year Later / S. Ekpanyapong, C. Bunchorntavakul, K.R. Reddy. J Viral Hepat. 2022 Jan. Vol. 29 (1). Р. 4-20.
- Prakash R. Mechanisms, diagnosis and management of hepatic encephalopathy / R. Prakash, K.D. Mullen. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2010. Vol. 7 (9). Р. 515-525.
- Функціональні захворювання кишечника / [Г.В. Дзяк, В.І. Залєвський, Ю.М. Степанов]. Дніпропетровськ: ПП «Ліра ЛТД», 2004. 200 с.
- Методи обробки експериментальних даних з використанням MS Excel / [А.А. Горват, О.О. Молнар, В.В. Мінькович]. — Ужгород: Вид-во УжНУ «Говерла», 2019. 160 с.: іл.
- Rapid Turn From Cirrhosis to Encephalopathy Following COVID-19 Infection: A Cautionary Tale / [T. Chowdhury, J. Sultana, J. Dutta, N. Gousy, K.N. Hassan]. Cureus. 2022 Feb 10. Vol. 14 (2). e22089.
- Nervous system involvement after infection with COVID-19 and other coronaviruses / [Y. Wu, X. Xu, Z. Chen et al.]. Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Jul. Vol. 87. Р. 18-22.
- COVID-19-induced hepatic encephalopathy: a case report / [E. Gamboa, D. Montelongo, H. Berjaoui et al.]. Crit Care Shock. 2020. Vol. 23. Р. 154-157.
- Fasano A. All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases [version 1; peer review: 3 approved] / A. Fasano. F1000Research. 2020. Vol. 9 (F1000 Faculty Rev). 69.
- Zak-Golab A. Gut Microbiota, Microinflammation, Metabolic Profile, and Zonulin Concentration in Obese and Normal Weight Subjects / A. Zak-Golab, P. Kocelak, M. Aptekorz. Hindawi Publishing Corporation. International Journal of Endocrinology. 2013. Article ID 674106. 9 pages.
- Zonulin, a marker of gut permeability, is associated with mortality in a cohort of hospitalised peruvian COVID-19 patients / [L.A. Palomino-Kobayashi, B. Ymaña, J. Ruiz, A. Mayanga-Herrera, M.F. Ugarte-Gil, M.J. Pons]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. Vol. 12. Р. 1000291.
- Ghosh G. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Patients With Cirrhosis / G. Ghosh, A.B. Jesudian. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019 Mar-Apr. Vol. 9 (2). Р. 257-267.
- Serum zonulin levels in patients with liver cirrhosis: Prognostic implications / [T.A. Voulgaris, D. Karagiannakis, E. Hadziyannis et al.]. World J Hepatol. 2021 Oct 27. Vol. 13 (10). 1394-1404.
- Serum Zonulin in HBV-Associated Chronic Hepatitis, Liver Cirrhosis, and Hepatocellular Carcinoma / [X. Wang, M.M. Li, Y. Niu et al.]. Dis Markers. 2019 Aug.14. Vol. 2019. Р. 5945721.