Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 58, №2, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Печінкова енцефалопатія: механізм формування і сучасні методи лікування
Авторы: Тетяна Чистик
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
При хронічних захворюваннях печінки порушується її детоксикуюча функція, що призводить до підвищення рівня амонію в крові. Гіперамоніємія активує зірчасті клітини печінки, які виробляють білки сполучної тканини, унаслідок чого виникає посилене колагеноутворення і фіброзування печінки. Амоній проникає через гематоенцефалічний бар’єр і в астроцитах метаболізується до глутаміну, що супроводжується підвищенням клітинної осмолярності та гідратації астроцитів, зниженням синтезу аденозинтрифосфату і розвитком гіпоенергетичного стану клітин. Підвищується концентрація ароматичних амінокислот і знижується вміст амінокислот з бічним ланцюгом, які впливають на синтез дофаміну, норадреналіну і серотоніну. Усе це викликає розвиток печінкової енцефалопатії, яка характеризується прогресуючим наростанням когнітивних порушень (зниження пам’яті, уваги, концентрації, інтелекту, здатності до рахування), розладами свідомості, мовлення. Гепа-Мерц — препарат, що внесений до рекомендацій Європейської та Американської асоціації з вивчення захворювань печінки для лікування печінкової енцефалопатії. Гепа-Мерц підсилює метаболізм аміаку, зменшує клінічні симптоми печінкової енцефалопатії, поліпшує функцію ендотелію і внутрішньопечінковий кровотік, сприяє деактивації зірчастих клітин, завдяки чому гальмується фіброз печінки. Ефективність і безпека препарату Гепа-Мерц для лікування печінкової енцефалопатії доведена результатами численних клінічних досліджень.
In chronic diseases of the liver, its detoxification function is disturbed, which leads to an increase in the blood level of ammonium. Hyperammonemia activates hepatic stellate cells that produce connective tissue proteins, resulting in increased collagen formation and liver fibrosis. Ammonia penetrates the blood-brain barrier and is metabolized to glutamine in astrocytes, which is accompanied by an increase in cellular osmolarity and hydration of astrocytes, a decrease in the adenosine triphosphate synthesis, and the development of a hypoenergetic state of cells. The concentration of aromatic amino acids increases and the content of amino acids with a side chain decreases that affects the synthesis of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. All this causes the development of hepatic encephalopathy, which is characterized by a progressive increase in cognitive impairment (a decrease in memory, attention, concentration, intelligence, ability to count), disorders of consciousness, speech. Hepa-Merz is a drug recommended by the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepa-Merz enhances ammonia metabolism, reduces the clinical symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy, improves endothelial function and intrahepatic blood flow, promotes the deactivation of stellate cells, due to which liver fibrosis is inhibited. The effectiveness and safety of Hepa-Merz for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy has been proven by the results of numerous clinical studies.
печінкова енцефалопатія; хронічні захворювання печінки; гіперамоніємія; Гепа-Мерц
hepatic encephalopathy; chronic liver diseases; hyperammonemia; Hepa-Merz
Патогенез печінкової енцефалопатії: у фокусі гіперамоніємія
/88.jpg)
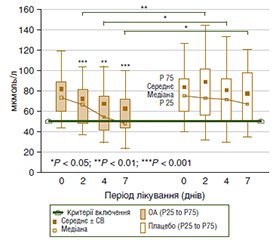
Гепа-Мерц — патогенетичне лікування печінкової енцефалопатії
/88_2.jpg)
Гепа-Мерц — доведена ефективність і безпека лікування печінкової енцефалопатії
/90.jpg)
/91.jpg)
Висновки
- Bismuth M, Funakoshi N, Cadranel JF, Blanc P. Hepatic encephalopathy: From pathophysiology to therapeutic management. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;23:8-22.
- Butterworth RF. Editorial: Rifaximin and minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:317-8.
- Ferenci P et al. Hepatic encephalopathy: definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantifi cation: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology. 2002;5:716-721.
- Elwir S, Rahimi RS. Hepatic encephalopathy: an update on the pathophysiology and therapeutic options. Clin Transl Hepatol. 2017;5(2):142-151. https://doi.org/10.14218/JCTH.2016.00069.
- Rahimi RS, Rockey DC. Novel ammonia-lowering agents for hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Liver Dis. 2015;19(3):539-549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2015.04.008.
- Sussman NL. Treatment of overt hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Li–ver Dis. 2015;19(3):551-563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2015.04.005.
- Sheasgreen C, Lu L, Patel A. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of hepatic encephalopathy. Inflammopharmacology. 2014;22(6):319-326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-014-0217-9.
- Blauenfeldt RA, Olesen SS, Hansen JB et al. Abnormal brain processing in hepatic encephalopathy: Evidence of cerebralreorganization? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;22:1323-30.
- Chen SJ, Wang LJ, Zhu Q et al. Effect of H pylori infection and its eradication on hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:1914-8.
- Bajaj JS, Pinkerton SD, Sanyal AJ, Heuman DM. Diagnosis and treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy to prevent motor vehicle accidents: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Hepatology. 2012 Apr;55(4):1164-71.
- Montgomery JY, Bajaj JS. Advances in the evaluation and management of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Cur Gastroenterol Rep. 2011;13:26-33.
- Reddy PV, Rama Rao KV, Norenberg MD. Inhibitors ofthe mitochondrial permeability transition reduce ammonia-induced cell swelling in cultured astrocytes. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87:2677-85.
- Mardini H, Smith FE, Record CO, Blamire AM. Magnetic re–sonance quantification of water and metabolites in the brain of cirrho–tics following induced hyperammonaemia. J Hepatol. 2011;54:1154-60.
- Donato F, Gelatti U, Limina RM, Fattovich G. Souther Europe as an example of interaction between various enviror mental factor: a systemic revoew of the epidemiologic evidence. Oncogene. 2006;25:3756-3770.
- Jalan R, De Chiara F, Balasubramaniyan V. et al. Ammonia produces pathological changes in human hepatic stellate cells and is a target for therapy of portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2016;64(4): 823-833.
- Lindquist JN, Parsons CJ, Stefanovic B, Brenner DA. Regulation of alpha1(I) collagen messenger RNA decay by interactions with alphaCP at the 3’-untranslated region. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:23822-29.
- Benyon RC, Iredale JP. Is liver fibrosis reversible? Gut. 2000;46:443-46.
- Arthur M.J. Fibrogenesis II. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000;279:G245-G249.
- Arthur MJ. Reversibility of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis following treatment for hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:1525-28.
- Jiang Q, Xue-Hua J, Ming-Hua Z. L-ornithine-L-aspartate in the management of hepatic encephalopathy: meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24(1):9-14.
- Рetersen KU. Options in the treatment of hepatic encephalo–pathy. Med Monatsschr Pharm. 2015;38(5):160-164.
- Butterworth RF, Canbay A. Hepatoprotection with using of L-ornithine-L-aspartate at nonalcocholic fatty liver disease. Digestive Diseases. 2018.
- De Bandt JP, Cynober LA. Amino acids with anabolic properties. Curr Opin Nutr Metab Care. 1998;(3)1:263-272.
- Kircheis G, Wettstein M, Dahl S, Häussinger D. Clinical efficacy of L-ornithine-L-aspartate in the management of hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2002;17(4):453-462.
- Stauch S, Kircheis G, Adler G, Beckh K, Ditschuneit H, Görtelmeyer R et al. Oral L-ornithine-L-aspartate therapy of chro–nic hepatic encephalopathy: results of a placebo-controlled double-blind study. J Hepatol. 1998;28(5):856-64. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(98)80237-7.
- Bai M, He C, Yin Z., Niu J., Wang Z., Qi X et al. Randomised clinical trial: L-ornithine-L-aspartate reduces significantly the increase of venous ammonia concentration after TIPSS. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 40(1):63-71.
- Grungreiff K, Lambert-Baumann J. Die Medizinische Welt. 2001;52:219-226.
- Zheng MH, Sun DQ, Jiang Q et al. Pharmacotherapy for Hepatic encephalopathy: view of Evidence-Based Medicine. J Liver. 2011;1(1):23-28.
- Ong JP, Oehler G., Krüger-Jansen C, Lambert-Baumann J, Younossi ZM. Oral L-ornithine-L-aspartate improves health-related quality of life in cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy: an open-label, prospective, multicentre observational study. Clin Drug Investig. 2011;31(4):213-20.
- Goh ET, Stokes CS, Sidhu SS, Vilstrup H, Gluud LL, Morgan MY. L-ornithine L-aspartate for prevention and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy in people with cirrhosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 May 15;5:CD012410. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012410.pub2.
- Alvares-da-Silva MR, de Araujo A, Vicenzi JR, da Silva GV, Oliveira FB, Schacher F et al. Oral l-ornithine-l-aspartate in minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Hepatol Res. 2014;44(9):956-963.
- American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 practice guideline by the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. J. Hepatol. 2014;61(3):642-659.

/89.jpg)
/89_2.jpg)
/90_2.jpg)