Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» Том 20, №4, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Проблемні питання діагностики та лікування синдрому Бурхаве
Авторы: V.S. Zhukovskiy, I.R. Trutyak, Ya.M. Pidhirnyi, Zh.V. Filip, M.V. Pankiv, V.S. Kozopas
Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, Lviv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
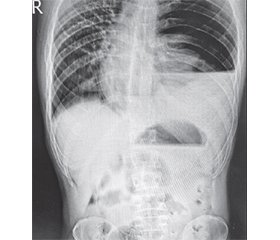
Синдром Бурхаве є рідкісним станом із захворюваністю 3,1/1 000 000 на рік, має високий рівень смертності через пізню діагностику та труднощі в лікуванні. Мета: привернути увагу лікарів до різноманітності клінічних проявів синдрому Бурхаве, що ускладнює ранню діагностику та прийняття рішень. Наведено клінічне спостереження двох пацієнтів із синдромом Бурхаве. Один хворий госпіталізований через 7 годин після появи болю у верхньому боці зліва, нудоти, блювання. При клінічному огляді, ультразвуковій діагностиці та рентгенологічному дослідженні патології не виявлено. Проте через 3 години стан хворого різко погіршився, з’явилася емфізема шиї та грудної клітки. Рентгенологічно виявлено лівосторонній пневмогемоторакс. При торакотомії в нижній третині стравоходу на його лівій латеральній стінці виявлений розрив довжиною 3,5 см, який було зашито. Грудну порожнину та середостіння очищено і дреновано за допомогою трубок. Сформовано гастростому. Післяопераційний період ускладнився поліорганною недостатністю та сепсисом. Пацієнт перебував у відділенні інтенсивної терапії 29 днів. На 46-ту добу рана стравоходу зажила, хворий виписаний на амбулаторне спостереження. Інший пацієнт був госпіталізований через 3 години після початку захворювання з лівостороннім пневмогемотораксом та симптомами гострого живота. Встановлено грудну трубку ліворуч, під тиском виділилася темно-коричнева рідина. Клінічні симптоми перитоніту спонукали хірургів до термінової лапаротомії, під час якої патології органів черевної порожнини не виявлено. Лише при комп’ютерній томографії діагностували розрив стравоходу. Внаслідок пізньої операції розвинулись інфекційні ускладнення та сепсис, що призвело до смерті хворого.
Boerhaave’s syndrome is a rare disease with an incidence of 3.1/1,000,000 per year, has a high mortality rate due to late diagnosis and difficulty in treatment. The purpose of the message is to draw the attention of doctors to the variety of clinical manifestations of Boerhaave’s syndrome, which complicates early diagnosis and decision making. Clinical observation of two patients with Boerhaave’s syndrome is presented. One patient was hospitalized 7 hours after the onset of pain in the upper left side, nausea, vomiting. Clinical examination, ultrasound and chest X-ray revealed no pathology. However, after 3 hours, the patient’s condition deteriorated sharply, emphysema of the neck and chest appeared. X-ray revealed left-sided pneumohemothorax. Thoracotomy revealed a 3.5-cm long rupture in the lower third of the esophagus on its left lateral wall, which was sutured. The chest cavity and mediastinum are debrided and drained using tubes. A gastrostomy was formed. The postoperative period was complicated by multiple organ failure and sepsis. Patient was in the intensive care unit for 29 days. The esophageal wound healed on the 46th day and the patient was discharged for outpatient observation. Another patient was hospitalized three hours after onset of illness with a left-sided pneumohemothorax and acute abdomen symptoms. Chest tube on the left was placed and a dark brown liquid released under pressure. The peritonitis clinical symptoms prompted surgeons to perform urgent laparotomy during which no pathology of the abdominal organs was detected. Only after computed tomography, a rupture of the esophagus was diagnosed. As a result of delayed surgery, infection complications and sepsis developed, which led to the patient’s death.
синдром Бурхаве; розрив стравоходу; діагностика; лікування; огляд
Boerhaave’s syndrome; rupture of the esophagus; diagnosis; treatment; review
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Chirica M, Kelly MD, Siboni S, et al. Esophageal emergencies: WSES guidelines. World J Emerg Surg. 2019;14:26. doi: 10.1186/s13017-019-0245-2.
- Pezzetta E, Kokudo T, Uldry E, et al. The surgical management of spontaneous esophageal perforation (Boerhaave’s syndrome) — 20 years of experience. Biosci Trends. 2016;10:120-4. doi: 10.5582/bst.2016.01009.
- Hashmi MAR, El-Badawy M, Agha A. Suspecting a fatal condition on a plain chest radiograph; Boerhaave syndrome. Scott Med J. 2021 Feb;66(1):46-48. doi: 10.1177/0036933020961181.
- Kakar N, Smith HC, Shadid AM. Prolonged Emesis Cau-sing Esophageal Perforation: A Case Report. Cureus. 2022 May 4;14(5):e24720. doi: 10.7759/cureus.24720.
- Aref H, Yunus T, Alhallaq O. Laparoscopic Management of Boerhaave’s syndrome: a case report with an intraoperative video. BMC Surg. 2019 Aug 13;19(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12893-019-0576-7.
- Vidarsdottir H, Blondal S, Alfredsson H, Geirsson A, Gudbjartsson T. Oesophageal perforations in Iceland: a whole population study on incidence, aetiology and surgical outcome. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010 Dec;58(8):476-80. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1250347.
- Allaway MGR, Morris PD, Sinclair BJ, Richardson AJ, Johnston ES, Hollands MJ. Management of Boerhaave syndrome in Australasia: a retrospective case series and systematic review of the Australasian literature. ANZ Journal of Surgery. 2020;91(7–8):1376-1384. doi.org/10.1111/ans.16501.
- Martínez-García A, Pérez-García K, Pérez-Palenzuela J, Sosa-Esquivel G, Díaz-Calderín JM. Boerhaave syndrome with double esophageal perforation. About a case. Cir Cir. 2021;89(S1):97-101. doi: 10.24875/CIRU.20001332.
- De Schipper JP, Pull ter Gunne AF, Oostvogel HJ, van Laarhoven CJ. Spontaneous rupture of the oesophagus: Boerhaave’s syndrome in 2008. Literature review and treatment algorithm. Dig Surg. 2009;26(1):1-6. doi: 10.1159/000191283.
- Puerta Vicente A, Priego Jiménez P, Cornejo López MÁ, García-Moreno Nisa F, Rodríguez Velasco G, et al. Management of Esophageal Perforation: 28-Year Experience in a Major Referral Center. Am Surg. 2018 May 1;84(5):684-689.
- Lieu MT, Layoun ME, Dai D, Soo Hoo GW, Betancourt J. Tension hydropneumothorax as the initial presentation of Boerhaave syndrome. Respir Med Case Rep. 2018 Jul 31;25:100-103. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2018.07.007.
- Tarazona MAD, Chaves CER, Mateus JFI, Comba FAR, Rosso JD, Uribe MCA. Boerhaave syndrome: Successful conservative treatment. Case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023 Jun;107:108289. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108289.
- Derbes VJ, Mitchell RE Jr. Hermann Boerhaave’s Atrocis, nec descripti prius, morbi historia, the first translation of the classic case report of rupture of the esophagus, with annotations. Bull Med Libr Assoc.1955;43(2):217-240.
- Barrett NR. Spontaneous perforation of the esophagus; review of the literature and report of three new cases. Thorax. 1946;1:48-70. doi: 10.1136/thx.1.1.48.
- Catarino Santos S, Barbosa B, Sá M, Constantino J, Casimiro C. Boerhaave’s syndrome: a case report of damage control approach. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019;58:104-107. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.04.030.
- Haba Y, Yano S, Akizuki H, Hashimoto T, Naito T, Hashiguchi N. Boerhaave syndrome due to excessive alcohol consumption: two case reports. Int J Emerg Med. 2020;13(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12245-020-00318-5.
- Ibrahim-Zada I, Ernest P, Moore EE. Intrathoracic transmural esophageal perforation (Boerhaave’s syndrome): Challenges in management of the delayed presentation. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018 Sep;85(3):644-645. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000001958.
- Harikrishnan S, Murugesan CS, Karthikeyan R, Manickavasagam K, Singh B. Challenges faced in the management of complicated Boerhaave syndrome: a tertiary care center experience. Pan Afr Med J. 2020 Jun 3;36:65. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2020.36.65.23666.
- Loftus IA, Umana EE, Scholtz IP, McElwee D. Mackler’s Triad: An Evolving Case of Boerhaave Syndrome in the Emergency Department. Cureus. 2023 Apr 22;15(4):e37978. doi: 10.7759/cureus.37978.
- Rokicki M, Rokicki W, Moj M, et al. Boerhaave Syndrome — over 290 years of surgical experiences. Can the disorder recur? Pol Przegl Chir. 2018;91(3):27-29.
- Tzeng CH, Chen WK, Lu HC, Chen HH, Lee KI, et al. Challenges in the diagnosis of Boerhaave syndrome: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jan;99(2):e18765. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018765.
- Chirica M, Bonavina L. Esophageal emergencies. Minerva Surg. 2023 Feb;78(1):52-67. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5691.22.09781-7.
- Sulpice L, Dileon S, Rayar M, Badic B, Coud JK, et al. Conservative surgical management of Boerhaave’s syndrome: experience of two tertiary referral centers. Int J Surg. 2013;11(1):64-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2012.11.013.
- Yoo SM, Chun EJ, Lee HY, et al. Computed tomography diagnosis of nonspecific acute chest pain in the emergency department: from typical acute coronary syndrome to various unusual mimics. J Thorac Imaging. 2017;32:26-35.
- Gupta RK, Sah PL, Sapkota S. Atypical presentation of Boerhaave’s syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2012;2012:bcr2012006368. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2012-006368.
- Oh MK, Jeon WJ, Cho SY, Kwon YD, Kim KN. Development of bilateral tension pneumothorax under anesthesia in a Boerhaave’s syndrome patient — a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2016;69(2):175-80. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2016.69.2.175.
- Ceriz T, Diegues A, Lagarteira J, Terras Alexandre R, Carrascal A. Boerhaave’s Syndrome: A Case Report. Cureus. 2022 Apr 5;14(4):e23836. doi: 10.7759/cureus.23836.
- Salvador-Ibarra IJ, Pizaña-Davila A. Boerhaave syndrome. Case report and literature review. Cir Cir. 2021;89(S2):26-30. doi: 10.24875/CIRU.21000010.
- Elliott JA, Buckley L, Albagir M, Athanasiou A, Murphy TJ. Minimally invasive surgical management of spontaneous esophageal perforation (Boerhaave’s syndrome). Surg Endosc. 2019 Oct;33(10):3494-3502. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-06863-2.
- Abbott J, Tinsley A, Campbell D, Dykes T, Moyer M. Water-soluble contrast for the diagnosis of esophageal perforation: a note of caution. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:S206-S207.
- Debiche S, Snene H, Attia M, Ben Abdelghani K, Ben Salah N, et al. Pneumomediastinum and vomiting: Which approach to diagnosis? A case report. Rev Mal Respir. 2022 Oct;39(8):726-730 (in French). doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2022.08.004.
- Morgan CT, Maloney JD, Decamp MM, McCarthy DP. A narrative review of primary spontaneous pneumomediastinum: a poorly understood and resource-intensive problem. J Thorac Dis. 2021 Jun;13(6):3721-3730. doi: 10.21037/jtd-21-193.
- Anand R, Puckett Y, Ronaghan CA. Above and Below the Diaphragm: A Previously Undescribed Case of Recurrent Boerhaave Syndrome Diagnosed with Computerized Tomography Esophagram. Cureus. 2022;14(4): e24015. doi: 10.7759/cureus.24015.
- Ali D, Detroz A, Gorur Y, Bosquée L, Cardos B, et al. Abrupt Severe Chest Pain and Vomiting: Remember to Think of a Ruptured Oesophagus (Boerhaave Syndrome). Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2019 Oct 4;6(10):001265. doi: 10.12890/2019_001265.
- Halitim P, Weisenburger G, Bunel-Gourdy V, Godet C, Salpin M, et al. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum. Rev Mal Respir. 2022 Mar;39(3):228-240 (in French). doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2021.12.004.
- Turner AR, Turner SD. Boerhaave Syndrome. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430808.
- Tellechea JI, Gonzalez JM, Miranda-García P, Culetto A, D’Journo XB, et al. Role of Endoscopy in the Management of Boerhaave Syndrome. Clin Endosc. 2018 Mar;51(2):186-191. doi: 10.5946/ce.2017.043.
- Chalikonda D, Yoo J, Johnson D, Tofani C. Boerhaave Syndrome Causing Bilateral Empyemas. ACG Case Rep J. 2019 Sep 2;6(9):e00203. doi: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000203.
- Aiolfi A, Micheletto G, Guerrazzi G, Bonitta G, Campanelli G, Bona D. Minimally invasive surgical management of Boerhaave’s syndrome: a narrative literature review. J Thorac Dis. 2020 Aug;12(8):4411-4417. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-1020.
- Petousis S, Margioula-Siarkou C, Lorenzi B, et al. High mortality rate of oesophageal perforation is associated with delayed hospital admission: a prospective observational case series study. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2020;83(1):11-14.
- Kita R, Kobayashi H, Nakao K, Iwaki K, Kondo M, Kaihara S. Three Cases of Boerhaave’s Syndrome Treated via Laparoscopic Transhiatal Esophageal Repair. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2022 Jun 17;16(2):406-412. doi: 10.1159/000525011.
- Pickering O, Pucher PH, De’Ath H, Abuawwad M, Kelly J, et al. Minimally Invasive Approach in Boerhaave’s Syndrome: Case Series and Systematic Review. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2021 Nov;31(11):1254-1261. doi: 10.1089/lap.2020.0751.
- Lee HL, Cho JY, Cho JH, Park JJ, Kim CG, et al. Efficacy of the Over-the-Scope Clip System for Treatment of Gastrointestinal Fistulas, Leaks, and Perforations: A Korean Multi-Center Study. Clin Endosc. 2018 Jan;51(1):61-65. doi: 10.5946/ce.2017.027.
- Al-Zahir AA, AlSaif OH, AlNaimi MM, Almomen SAM, Meshikhes AN. Boerhaave’s Syndrome: Delayed Management Using Over-the-Scope Clip. Am J Case Rep. 2019 Jun 10;20:816-821. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.916320.
- Kuwabara J, Watanabe Y, Kojima Y, Higaki N, Ikeda Y, et al. Successful closure of spontaneous esophageal rupture (Boerhaave’s syndrome) by endoscopic ligation with snare loops. Springerplus. 2016 Jun 29;5(1):921. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-2624-4.
- Saxena P, Khashab MA. Endoscopic management of esophageal perforations: who, when, and how? Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2017;15(1):35-45.
- Kopelman Y, Abu Baker F, Troiza A, Hebron D. Boerhaave syndrome in an elderly man successfully treated with 3-month indwel-ling esophageal stent. Radiol Case Rep. 2018;13(5):1084-1086. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2018.04.026.
- Chen A, Kim R. Boerhaave syndrome treated with endoscopic suturing. VideoGIE. 2019;4(3):118-119. doi: 10.1016/j.vgie.2018.12.005.
- Luttikhold J, Pattynama LMD, Seewald S, Groth S, Morell BK, et al. Endoscopic vacuum therapy for esophageal perforation: a multicenter retrospective cohort study. Endoscopy. 2023 Sep;55(9):859-864. doi: 10.1055/a-2042-6707.
- Scharl M, Stanek N, Kröger A, Bauerfeind P, Gubler C. Successful treatment of a proximal esophageal rupture with a luminal sponge. Endoscopy. 2015;47 Suppl. 1 UCTN:E293-4. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1392029.
- Bani Fawwaz BA, Gerges P, Singh G, Rahman SH, Al-Dwairy A, et al. Boerhaave Syndrome: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review. Cureus. 2022 May 23;14(5):e25241. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25241.
- Shahriarirad R, Karoobi M, Shekouhi R, Ebrahimi K, Ranjbar K, et al. Esophageal perforation etiology, outcome, and the role of surgical management — an 18-year experience of surgical cases in a referral center. BMC Surg. 2023 Jun 27;23(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s12893-023-02080-w.
- Loske G, Schorsch T, van Ackeren V, Schulze W, Müller CT. Endoscopic vacuum therapy in Boerhaave’s syndrome with open-pore polyurethane foam and a new open-pore film drainage. Endoscopy. 2015;47 Suppl. 1 UCTN:E410-1. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1392597.
- Wang J, Wang D, Chen J. Diagnostic challenge and surgical management of Boerhaave’s syndrome: a case series. J Med Case Rep. 2021 Nov 8;15(1):553. doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-03080-1.
- Śnieżyński J, Wilczyński B, Skoczylas T, Wallner GT. Successful Late Endoscopic Stent-Grafting in a Patient with Boerhaave Syndrome. Am J Case Rep. 2021 Aug 13;22:e931629. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.931629.
- Truyens M, Hufkens E, Van Geluwe B, Vergauwe P, Van Moerkercke W. Boerhaave’s syndrome: successful conservative treatment in two patients. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2020 Oct-Dec;83(4):654-656.
- DeVivo A, Sheng AY, Koyfman A, Long B. High risk and low prevalence diseases: Esophageal perforation. Am J Emerg Med. 2022 Mar;53:29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.12.017.