Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 20, №4, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Актуальність використання вітаміну D3 з профілактичною метою в дітей раннього віку
Авторы: S.S. Levenets, S.O. Nykytyuk, T.V. Hariyan, V.H. Dzhyvak
I. Horbachevsky Ternopil National Medical University, Ternopil, Ukraine
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
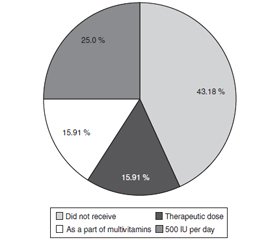
Актуальність. Актуальність роботи полягає в розумінні значення вітаміну D3 для організму дитини та його правильному використанні з профілактичною метою. Достатня кількість вітаміну D3 важлива для належної мінералізації кісток у дітей та формування імунної відповіді, а також правильного функціонування всіх органів і систем. Мета: проаналізувати дотримання батьками призначень лікарів щодо застосування вітаміну D3 для антенатальної та постнатальної профілактики, а також харчове забезпечення вітаміном D і кальцієм. Матеріали та методи. У дітей віком до 2 років проаналізовано правильність медичних призначень щодо використання вітаміну D3 з профілактичною метою на основі нормативних документів Міністерства охорони здоров’я України. Було використано метод випадкової вибірки з анонімним опитуванням матерів дітей щодо застосування різних схем вітаміну D3 з профілактичною метою та споживання вітаміну D3 жінками під час вагітності. Результати. Проаналізовано материнські та дитячі фактори, що впливають на забезпечення дітей вітаміном D. Було оцінено результати антенатального споживання вітамінів у вагітних жінок, а також проаналізовано схеми профілактичного застосування вітаміну D3 у дітей раннього віку. Висновки. Виявлено, що більшість дітей мали неонатальний ризик дефіциту вітаміну D. Багато дітей отримували вітамін D для профілактики мальнутриції до 1 року, переважно в осінньо-зимово-весняний сезон, за винятком літніх місяців. Деякі діти отримували вітамін D нерегулярно або взагалі не отримували вітамін D3 з профілактичною метою. Добове споживання вітаміну D та кальцію з їжі є менш достатнім для дітей. Найбільша кількість кальцію в раціоні дітей надходить з молочних продуктів: молока, дитячих сумішей, сиру, йогурту, тоді як рівень вітаміну D3 не залежить від споживання молочних продуктів.
Background. The relevance of the work is to understand the role of vitamin D3 for the child’s body and its correct use for preventive purposes. A sufficient amount of vitamin D3 is important for proper bone mineralisation in children and the formation of the immune system response, as well as the correct functioning of all organs and systems. The purpose was to analyse parental compliance with physicians’ prescriptions on the use of vitamin D3 for antenatal and postnatal prophylaxis, and nutritional provision with vitamin D and calcium. Materials and methods. In children under 2 years of age, we analysed the correctness of medical prescriptions on vitamin D3 administration for prophylactic purposes based on the regulatory documents of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine. The method of random sampling was used with an anonymous survey of mothers of children regarding the use of different schemes of vitamin D3 for prophylactic purposes and vitamin D3 intake by women during pregnancy. Results. The maternal and infant factors affecting the provision of children with vitamin D were analysed. Results of antenatal vitamin intake in pregnant women were evaluated, and schemes of preventive use of vitamin D3 in young children were analysed. Conclusions. It was found that most children had a neonatal risk of vitamin D deficiency. Many children received vitamin D to prevent malnutrition before the age of 1 year, mainly in the autumn-winter-spring season, excluding summer months. Some children received vitamin D irregularly or did not receive vitamin D3 for preventive purposes at all. The daily intake of vitamin D and calcium from food is less than adequate for children. The largest amount of calcium in children’s diets comes from dairy products: milk, infant formula, cheese, yoghurt, while vitamin D3 intake is independent of dairy consumption.
діти; вітамін D3; профілактика; добавки
children; vitamin D3; prevention; supplementation
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Bellavia D, Costa V, DeLuca A, et al. Vitamin D level between calcium-phosphorus homeostasis and immune system: new perspective in osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2024;22:599-610. doi: 10.1007/s11914-016-0331-2.
- Zittermann A, Pilz S, Berthold HK. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D response to vitamin D supplementation in infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical intervention trials. Eur J Nutr. 2020;59:359-369. doi: 10.1007/s00394-019-01912-x.
- Dai Z, McKenzie JE, McDonald S, Baram L, Page MJ, et al. Assessment of the methods used to develop vitamin D and calcium recommendations — a systematic review of bone health guidelines. Nutrients. 2021;13:2423. doi: 10.3390/nu13072423.
- Gnoli M, Brizola E, Tremosini M, DiCecco A, Sangiorgi L. Vitamin D and bone fragility in individuals with osteogenesis imperfecta: a sco–ping review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(11):9416. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119416.
- Protsailo MD, Dzhyvak VG, Tkachuk VV, Horishnyi IM, Voroncova TO, Kucher SV, Khlibovska OI. Clinical aspects of the tubular bones epiphyseal plate malformations (literature review). Fam Med Eur Pract. 2024;3:77-83. doi: 10.30841/2786-720X.3.2024.313979.
- Saadon H. Vitamin D deficiency in childhood: a review. Univ Thi-Qar J Sci. 2024;11(1):176-184. doi: 10.32792/utq/utjsci/v11i1.1230.
- Buttriss JL, Lanham-New SA, Steenson S, Levy L, Swan GE, et al. Implementation strategies for improving vitamin D status and increasing vitamin D intake in the UK: current controversies and future perspectives. Br J Nutr. 2021;21:1-21. doi: 10.1017/S0007114521002555.
- Charoenngam N, Ayoub D, Holick MF. Nutritional rickets and vitamin D deficiency: consequences and strategies for treatment and prevention. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2022;17:351-364. doi: 10.1080/17446651.2022.2099374.
- Pludowski P, Takacs I, Boyanov M, Belaya Z, Diaconu C, et al. Clinical practice in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of vitamin D deficiency: a Central and Eastern European expert consensus statement. Nutrients. 2022;14(7):1483. doi: 10.3390/nu14071483.
- Protsailo MD, Dzhyvak VH, Horishniy IM, Hariyan TV, Ku–cher SV, Prodan AM. Orthopedic manifestations of degenerative melanosis (clinical case report). Health Man. 2024;2:45-48. doi: 10.30841/2786-7323.2.2024.310019.
- Saponaro F, Saba A, Zucchi R. An update on vitamin D metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:6573. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186573.
- Wimalawansa SJ. Infections and autoimmunity — the immune system and vitamin D: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2023;15:3842. doi: 10.3390/nu15173842.
- Bishop EL, Ismailova A, Dimeloe S, Hewison M, White JH. Vitamin D and immune regulation: antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory. JBMR Plus. 2021;5(1). doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10405.
- Mailhot G, White JH. Vitamin D and immunity in infants and children. Nutrients. 2020;12(5):1233. doi: 10.3390/nu12051233.
- Evidence-based clinical practice guideline “Prevention and treatment of nutritional rickets”. 2023. 56 p. (in Ukrainian).
- Order No. 730 of April 17, 2023 “On approval of the Standards of medical care “Prevention and treatment of nutritional rickets”. 2023. 16 p. (in Ukrainian).
- Standards of medical care “Prevention and treatment of nutritional rickets”. 2023. 16 p. (in Ukrainian).
- Maretzke F, Bechthold A, Egert S, Ernst JB, Melo van Lent D, et al. Role of vitamin D in preventing and treating selected extraskeletal diseases — an umbrella review. Nutrients. 2021;12:969. doi: 10.3390/nu12040969.
- Zittermann A, Trummer C, Theiler-Schwetz V, Lerchbaum E, Marz W, Pilz S. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease: an updated narrative review. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:2896. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062896.
- Bouillon R, Manousaki D, Rosen C, Trajanoska K, Riva–deneira F, Richards JB. The health effects of vitamin D supplementation: evidence from human studies. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;18:96. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00593-z.
- Mochulska OM, Boyarchuk OR, Kinash MI, Vorontsova TO, Volianska LA. The effects of vitamins A, E, D, disorders of their metabolism and the assessment of level of vitamin security in children (literature review). Mod Pediatr. Ukraine. 2021;2(114):58-66. doi: 10.15574/SP.2021.114.58.
- Tiazhka OV, Selska ZV. The value of vitamin D in the prevention and treatment of exacerbations of bronchial asthma in children. Child’s Health. 2024;19(1). doi: 10.22141/2224-0551.19.1.2024.1663.
- Lautatzis ME, Keya FK, AlMahmud A, Tariq U, Lam C, et al. Maternal vitamin D supplementation and infantile rickets: secondary analysis of a randomized trial. Pediatrics. 2024;153(6). doi: 10.1542/peds.2023-063263.
- Janoušek J, Pilařová V, Macáková K, Nomura A, Veiga-Matos J, Silva DD, Mladěnka P. Vitamin D: sources, physiological role, biokinetics, deficiency, therapeutic use, toxicity, and overview of analytical methods for detection of vitamin D and its metabolites. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2022;59(8):517-554. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2022.2070595.
- Wimalawansa SJ, Weiss ST, Hollis BW. Integrating endocrine, genomic, and extra-skeletal benefits of vitamin D into national and regional clinical guidelines. Nutrients. 2024;16(22):3969. doi: 10.3390/nu16223969.
- Andrade M, Knight J, Bayram-Weston Z. Vitamin D: the “sunshine vitamin”, its role and the effects of deficiency. Nurs Times. 2024;120(4).
- Harvey N, Ward K, Agnusdei D, et al. Optimisation of vitamin D status in global populations. Osteoporos Int. 2024;35:1313-1322. doi: 10.1007/s00198-024-07127-z.
- Nykytyuk SO, Hariyan TV, Levenets SS. Hemorrhagic vasculitis in an adolescent induced by the COVID-19 virus. Mod Pediatr. Ukraine. 2024;(6):120-126. doi: 10.15574/SP.2024.6(142).120126.
- Nykytyuk SO, Kuchma PM, Kito VV, Hariyan TV, Yakymchuk YB. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome MIS-C in children after COVID-19 infection. Ukr J Perinatol Pediatr. 2023;96(4):128-135. doi: 10.15574/PP.2023.96.128.