Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 21, №7, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Експресія та поліморфізми гена IRS1, пов’язані з ризиком розвитку цукрового діабету 2-го типу в іракських пацієнтів
Авторы: Noor Q. Mudhaffer (1), Ismail A. Abdul Hassan (2)
(1) - Central Teaching Hospital of Pediatrics, Ministry of Health, Baghdad, Iraq
(2) - Institute of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology for Postgraduate Studies, University of Baghdad, Iraq
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
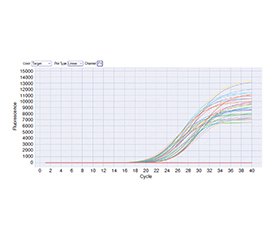
Актуальність. Цукровий діабет 2-го типу (ЦД2) — це складне метаболічне захворювання хронічного характеру. Однією з основних ланок патофізіології ЦД2 є субстрат інсулінового рецептора 1 (IRS1), що, як було показано, опосередковує майже весь спектр інсулінової сигналізації через відповідні сигнальні шляхи. Встановлено, що однонуклеотидний поліморфізм rs1801278 (Gly972Arg) в IRS1 пов’язаний iз порушенням інсулінової сигналізації та, отже, з підвищеним ризиком розвитку ЦД2 у деяких когортах. Однак мало що відомо про вплив цього поліморфізму в іракській популяції. Мета: встановлення зв’язку між поліморфізмом rs1801278 IRS1 i ризиком розвитку ЦД2 в іракських пацієнтів, а також оцінка експресії гена IRS1 при ЦД2 та у здорових осіб із контрольної групи. Матеріали та методи. У дослідження залучено 120 учасників: 60 хворих із діагнозом ЦД2 та 60 практично здорових осіб (контрольна група). Генотипування IRS1 rs1801278 було проведено за допомогою аналізу високої роздільної здатності, а експресію мРНК гена IRS1 оцінено з використанням кількісної полімеразної ланцюгової реакції в реальному часі зі зворотною транскрипцією. Частота генотипу й алелів, рівень експресії та зв’язок із перебігом захворювання визначені за допомогою відповідного статистичного аналізу. Результати. Частота алеля A (Arg) rs1801278 була вищою в пацієнтів із ЦД2 (38,3 %), ніж у контрольній групі (10,8 %), що вказувало на підвищений ризик (відношення шансів (ВШ) = 5,12, P < 0,0001). Генотипи GA та AA зустрічались частіше в пацієнтів із ЦД2 (GА: 36,6 %, AA: 20 %) порівняно з контрольною групою (GА: 15 %, AA: 3,3 %), що теж підтверджувало підвищений ризик (GА: ВШ = 4,61, P = 0,0006; AA: ВШ = 11,31, P = 0,0004). Експресія гена IRS1 була значно знижена в пацієнтів із ЦД2 із кратністю змін 0,6115 порівняно з контрольною групою (1,00). Це свідчить про можливе порушення інсулінової сигналізації на молекулярному рівні. Висновки. У дослідженні виявлено вірогідний зв’язок між поліморфним локусом IRS1 rs1801278 (Gly972Arg) та вищим ризиком ЦД2 в іракців. Зниження експресії гена IRS1 у пацієнтів із ЦД2 додатково підтверджує роль IRS1 у розвитку цього захворювання і можливість його використання як генетичного маркера для раннього виявлення та персоналізованого лікування ЦД2 в іракській популяції.
Background. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a complex metabolic disorder that is chronic in nature. One of the main players in the pathophysiology of T2DM is the insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1), which has been shown to mediate almost the entire spectrum of insulin signaling via downstream signaling pathways. A common single nucleotide polymorphism, rs1801278 (Gly972Arg), in IRS1 has been shown to be associated with impaired insulin signaling and therefore an increased risk of T2DM in a number of populations. However, little is known about the effect of this polymorphism in the Iraqi population. The purpose of this study: to determine the association between IRS1 rs1801278 polymorphism, the risk of T2DM in Iraqi patients, and to compare the expression of IRS1 gene in those with T2DM and healthy controls. Materials and methods. The study included 120 participants: 60 individuals diagnosed with T2DM and 60 apparently healthy individuals (healthy controls). Genotyping of IRS1 rs1801278 was performed using high resolution melting analysis, and the mRNA expression of the IRS1 gene was assesed using real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Genotype and alleles frequency, expression level and association with disease status were computed using appropriate statistical analyses. Results. The frequency of the A allele (Arg) of rs1801278 was higher in the T2DM patients (38.3 %) than in controls (10.8 %) and indicated an increased risk (OR = 5.12, P < 0.0001). The GA and AA genotypes were greater in T2DM patients (GA: 36.6 %, AA: 20 %) compared to controls (GA: 15 %, AA: 3.3 %) and conferred an increased risk (GA: OR = 4.61, P = 0.0006; AA: OR = 11.31, P = 0.0004). The expression of the IRS1 gene was significantly decreased in T2DM patients with fold change 0.6115 compared to healthy controls with fold change 1.00, suggesting that there may be impairment of insulin signaling at the molecular level. Conclusions. This study has identified a significant association between the IRS1 rs1801278 (Gly972Arg) polymorphic locus and higher risk of T2DM among Iraqis. The downregulation of IRS1 gene expression in T2DM patients further substantiates the role of IRS1 in the development and pathobiology of this disease and confirms the potential for IRS1 to be used as genetic marker for early detection and personalized management of T2DM in the Iraqi population.
ген IRS1; цукровий діабет 2-го типу; rs1801278; Gly972Arg; експресія генів; поліморфізм; іракська популяція; інсулінова сигналізація
IRS1 gene; type 2 diabetes mellitus; rs1801278; Gly972Arg; gene expression; polymorphism; Iraqi population; insulin signaling
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in diabetes prevalence and treatment from 1990 to 2022: a pooled analysis of 1108 population-representative studies with 141 million participants. Lancet. 2024;404(10467):2077-2093. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(24)02317-1.
- Tsokkou S, Tzintros ST, Konstantinidis I, Keramas A, Georgaki MN, et al. Assessment of environmental risk factors for gestational diabetes mellitus: a ten-year systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med. 2025;14(5):1646. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051646.
- Tremblay J, Hamet P. Environmental and genetic contributions to diabetes. Metabolism. 2019;100S:153952. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.153952.
- Singh A, Shadangi S, Gupta PK, Rana S. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: a comprehensive review of pathophysiology, comorbidities, and emerging therapies. Compr Physiol. 2025;15(1):e70003. doi: 10.1002/cph4.70003.
- Khalidah Salih Merzah. Evaluation of some biochemical parameters in Iraqi type 2 diabetes patients. Osol J Med Sci. 2024;17-25. doi: 10.69946/ojms/2024.02.02.
- Huda Mohammed, Dunya Fareed Salloom. Evaluation of interleukin-9 serum level and gene polymorphism in a sample of Iraqi type 2 diabetic mellitus patients. Meta Gene. 2021;27:100845. doi: 10.1016/j.mgene.2020.100845.
- Suhad M, Delan Y. Association of TCF7L2 rs7903146 polymorphism with the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) among Kurdish population in Erbil Province, Iraq. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2021;36(3):312-318. doi: 10.1007/s12291-020-00904-7.
- Buraczynska M, Swatowski A, Markowska-Gosik D, Kuczmaszewska A, Ksiazek A. Transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene polymorphism and complication/comorbidity profile in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;93(3):390-395. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.05.017.
- Albegali AA, Shahzad M, Mahmood S, Ullah MI. Genetic association of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS1, rs1801278) gene with insulin resistant of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Pakistani population. Mol Biol Rep. 2019;46(6):6065-6070. doi: 10.1007/s11033-019-05041-w.
- Yousef AA, Behiry EG, Allah WMA, Hussien AM, Abdelmoneam AA, et al. IRS1 genetic polymorphism (r.2963G>A) in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients associated with insulin resistance. Appl Clin Genet. 2018;11:99-106. doi: 10.2147/tacg.s171096.
- Li Q, Qiao Y, Wang C, Zhang G, Zhang X, Xu L. Associations between two single-nucleotide polymorphisms (rs1801278 and rs2943641) of insulin receptor substrate 1 gene and type 2 diabetes susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Endocrine. 2016;51(1):52-62. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0770-z.
- Rangel H, Fernandez G, Pestana J, Benítez G, Garcés MF. Polimorfismo gly972arg del gen IRS1 en pacientes con obesidad mórbida. Acta Cient Soc Venez Bioanalistas Especialistas. 2023;26(1):12-21. doi: 10.71034/svbe.2023.26.1.02.
- Thameem F, Puppala S, Schneider J, Bhandari B, Arya R, et al. The Gly972Arg variant of human IRS1 gene is associated with variation in glomerular filtration rate likely through impaired insulin receptor signaling. Diabetes. 2012;61(9):2385-2393. doi: 10.2337/db11-1078.
- Reed GH, Kent JO, Wittwer CT. High-resolution DNA melting analysis for simple and efficient molecular diagnostics. Pharmaco–genomics. 2007;8(6):597-608. doi: 10.2217/14622416.8.6.597.
- Sulaieva O, Yerokhovych V, Zemskov S, Komisarenko I, Gurianov V, et al. The impact of war on people with type 2 diabetes in Ukraine: a survey study. EClinicalMedicine. 2024;79:103008. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103008.
- Al-Rubaye AAH, Jasim WE, Mohsin AAH. Myonectin, irisin, apelin-13 and Elabela hormones levels as biomarkers for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Ukr Biochem J. 2024;96(4):17-24. doi: 10.15407/ubj96.04.017.
- Jellema A, Zeegers MP, Feskens EJ, Dagnelie PC, Mensink RP. Gly972Arg variant in the insulin receptor substrate-1 gene and association with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of 27 studies. Diabetologia. 2003;46(7):990-995. doi: 10.1007/s00125-003-1126-4.
- Haghani K, Bakhtiyari S. The study on the relationship between IRS1 Gly972Arg and IRS-2 Gly1057Asp polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes in the Kurdish ethnic group in West Iran. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2012;16(11):1270-1276. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2012.0160.
- Bhattacharjee A, Pranto SMAM, Ahammad I, Chowdhury ZM, Juliana FM, et al. High-risk genetic variants of human insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) infer structural instability and functional interference. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023;41(24):15150-15164. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2187232.
- Araújo EP, De Souza CT, Gasparetti AL, Ueno M, Boschero AC, et al. Short-term in vivo inhibition of insulin receptor substrate-1 expression leads to insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and increased adiposity. Endocrinology. 2005;146(3):1428-1437. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0778.
- Toyoshima Y, Nakamura K, Taguchi Y, Tokita R, Takeuchi S, et al. Deletion of IRS1 leads to growth failure and insulin resistance with downregulation of liver and muscle insulin signaling in rats. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):649. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84234-1.
- Yenzeel JH, Hassani HH. Expression of IRS1 gene in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus, in the third trimester. Iraqi J Sci. 2021; 787-792. doi: 10.24996/ijs.2021.62.3.9.
- Fröjdö S, Vidal H, Pirola L. Alterations of insulin signa–ling in type 2 diabetes: a review of the current evidence from humans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792(2):83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.10.019.
- Carvalho E, Jansson PA, Nagaev I, Wenthzel AM, Smith U. Insulin resistance with low cellular IRS1 expression is also associated with low GLUT4 expression and impaired insulin-stimulated glucose transport. FASEB J. 2001;15(6):1101-1103.